Enhancing Power System Resilience through Optimized Load-Shedding Strategies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/%20sijese.4.1.19Keywords:
Load shedding, resilience, IEEE 57-Bus RTS, power systemAbstract
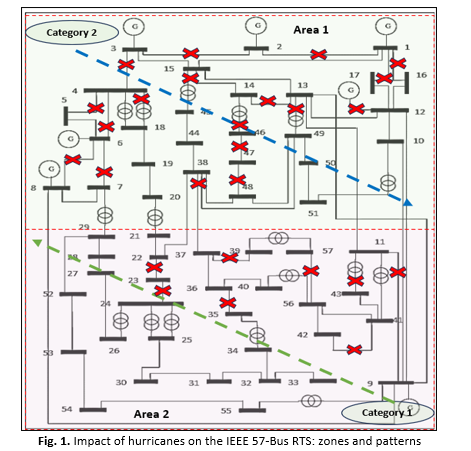
Electric power systems are critical to modern life, supporting essential services and economic activities. However, these systems are increasingly vulnerable to natural disasters such as hurricanes, which can severely damage infrastructure and disrupt power supply. The growing intensity and frequency of these events, driven by climate change, highlight the urgent need to enhance power system resilience. Load shedding is a vital mitigation strategy used to balance the supply and demand during extreme events, ensuring system stability and resilience which preventing widespread outages. Despite its importance, existing studies primarily focus on immediate impacts, with limited exploration of optimal load-shedding strategies to minimize power losses and enhanced resilience. This study introduces the Integrated Clonal Squirrel Search Evolutionary Programming (ICSSEP), a novel hybrid optimization technique that integrates Clonal Selection Optimization (CSO) and the Squirrel Search Algorithm (SSA) into the Evolutionary Programming (EP) algorithm. The ICSSEP algorithm addresses the limitations of traditional optimization methods, such as entrapment in local optima, by improving accuracy and efficiency. Using the IEEE 57-Bus Reliability Test System (RTS), the proposed method determines the optimal locations and sizes for load-shedding to minimize power losses and enhance system resilience. Two scenarios simulating hurricane impacts were analysed, focusing on line outages and their effects on system performance. The ICSSEP-based load-shedding strategy was applied, and pre- and post-load-shedding resilience indices were calculated. Results demonstrated significant improvements in resilience and substantial reductions in power losses across all scenarios and reactive power demands. For instance, at Bus 33 with a reactive power demand of 15 MVAr, power losses were reduced by 14.17 % in Scenario 1 and 40.17 % in Scenario 2 after optimization. It worth to mention that, ICSSEP effectively enhances the power system resilience and minimizes transmission losses, proving to be a robust tool for mitigating the adverse impacts of extreme events. Its adaptability to varying operational conditions makes it a promising solution for modern power systems. Future research should explore its application to larger networks and dynamic environments to further validate its scalability and effectiveness.
Downloads