Electrical Responses of Chitosan-based Biosensor Toward Cadmium Ions Adsorption
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijese.1.1.2634Keywords:
Chitosan, biosensors, heavy metal ions, cadmium, interdigitated electrodeAbstract
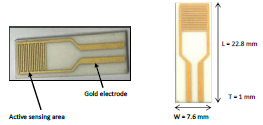
Chitosan-based biosensors has contributed to the advancement of bio-detection technologies, offering improved sensitivity and selectivity for the detection of various analytes, such as heavy metal ions. The presence of heavy metal ions in the environment poses a significant threat to human health, environmental quality, and ecosystem stability due to their carcinogenic and toxic properties. This study incorporates chitosan film in direct spatial contact with an interdigitated electrode to determine its electrical response. Chitosan films were soaked in cadmium ion solution in various concentrations before measuring the film's resistance, capacitance and impedance. Identification of circuit arrangement was done by employing the Nyquist plot. The results show that ionic concentration is directly proportional to films' adsorption, capacitance and conductivity. However, the impedance and resistance value decreased as the metal ion concentration increased. The findings suggest that chitosan film possesses the capability to adsorb cadmium ions, even at low concentrations. Additionally, alterations in the electrical properties of the film can serve as a reliable indicator of the concentration of ions present in the solution.
Downloads