Parameter Estimation Methods for Bivariate Copula in Financial Application
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijmaf.2.1.1021Keywords:
Bivariate copula, parameter estimation, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE), pseudo maximum likelihood (PML), Archimedean copulaAbstract
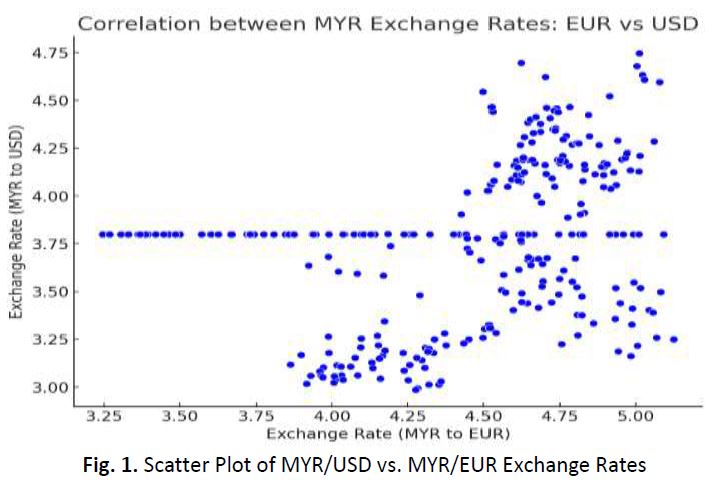
In the field of finance, understanding the dependencies between financial variables is crucial for effective risk management and decision-making. Copulas are powerful tools used to model these dependencies, enabling more accurate financial predictions and assessments. However, accurate estimation of copula parameters remains a significant challenge, impacting the reliability of the dependency structures modeled. This study addresses this problem by evaluating the effectiveness of four parameter estimation methods: maximum likelihood estimation, pseudo maximum likelihood, inversion of the rank correlation coefficient based on Kendall’s tau and Spearman’s rho. The objective is to determine which method provides the most accurate estimates for financial applications. The methodology involves a comparative analysis using exchange rate data for the Malaysian Ringgit against the U.S. Dollar and the Euro, covering the period from 1999 to 2023, sourced from Bank Negara Malaysia. Various copula families, including Gumbel, Clayton, Frank, Gaussian, and Student’s t, are employed to model the dependencies between these exchange rates. The study involves transforming the marginals of the sample data into uniform variates, estimating copula parameters, and evaluating the models' performance using the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) as a measure of goodness-of-fit. The principal results indicate that the Frank copula, exhibits the lowest RMSE, demonstrating superior performance in capturing the dependency structure of the data. This finding highlights the suitability of the Frank copula for financial risk management and decision-making. In conclusion, this analysis enhances the understanding of copula parameter estimation in finance, providing insights into the effectiveness of different methods and their practical applications in modeling financial dependencies.