Analytical Simulation of Magnetohydrodynamics Casson Blood Flow using CNTs in a Channel with Atherosclerosis Condition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/scbtrj.1.1.117Keywords:
Blood flow, carbon nanotubes, Laplace transformations, channel, Casson fluidAbstract
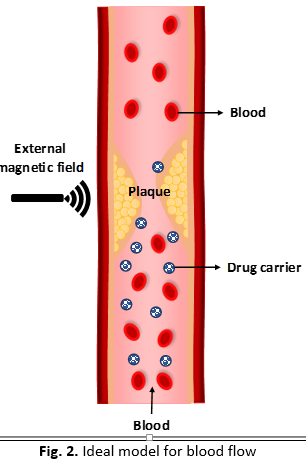
Atherosclerosis is a condition where the arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the buildup of plaque, which is made up of cholesterol, fat and other substances. This narrowing restricts blood flow and can lead to severe complications such as heart attacks and strokes. The biofluid dynamics of blood is commonly studied numerically using various numerical methods, which can lead to the inaccuracies of results. Therefore, the analytical solution is important as it can provide a verification to the approximate solutions obtained by numerical methods. The present study interested to discover the realm of blood rheology in analytical field by investigating the blood flow under the influences of nanoparticles (drug-carriers), porosity (plaque) and magnetic field (external source of energy). The Navier Stokes equations incorporating the Casson fluid model govern the fluid flow subjected to suitable initial and boundary conditions. The conversion of dimensional governing equations into dimensionless is conducted using relevant dimensionless variables, which are then employed by the Laplace transform to attain the analytical solutions. The results report that the addition of carbon nanotube (CNTs) significantly enhances the heat transfer and velocity of the blood, which can be an advantage in the process of plaque fragmentation. Besides, this analytical study of blood flow provides valuable theoretical insights into the fundamental principles governing cardiovascular physiology, guiding the development of medical devices and treatments and informing clinical decision-making.
Downloads