Development Of Enhanced Taguchi's T-Method Model in Predicting Energy Demand
Keywords:
Energy demand predictions, larger-the-better signal-to-noise ratio, prediction, Taguchi’s T-MethodAbstract
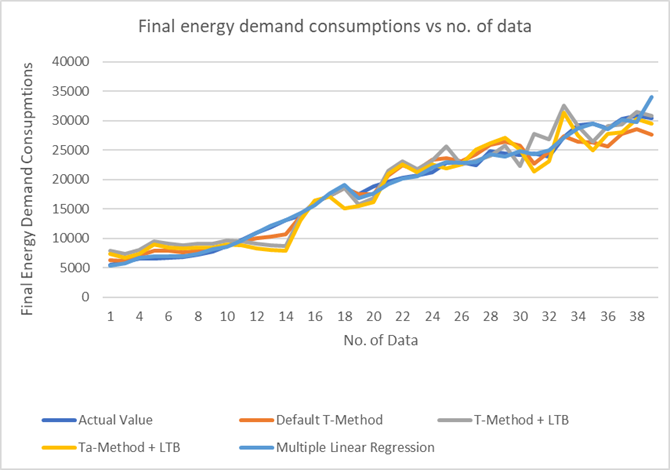
Energy is important for a country to grow and become a developed nation. Energy management will help a country to supply energy demand without any shortage or excess of energy. To manage energy, the government must know important aspects that lead to energy consumptions, such as growth domestic product (GDP) of the nation, energy supply, energy transformation, and energy consumptions. Here, prediction analysis will come in handy to predict the final energy consumptions. The Taguchi’s T-Method is one of the prediction analyses that may be used for this purpose as it is applicable in various fields. It can predict with a limited data sample, thus making it reliable and cost saving. It depends on history data to develop a prediction model by adapting signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and zero proportional concepts. Orthogonal Array is introduced in the Taguchi’s T-Method to optimise the model by eliminating variables that may reduce the accuracy of the prediction model. The Taguchi’s T-Method uses dynamic SNR that is not suitable for all types of predictions, and unit space selection in the middle position between the lowest and highest data will reduce the number of raw data. In this study, Ta-Method and larger-the-better signal-to-noise ratio (LTB SNR) were introduced to compare prediction accuracy of the current method with that of the default Taguchi’s T-Method. Three models were developed, namely default Taguchi’s T-Method, T-Method + LTB SNR, and Ta-Method + LTB SNR for three different case studies. The result showed the Ta-Method + LTB SNR had the most accurate prediction compared to the other models for mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) for predicting energy demand case study.
Downloads