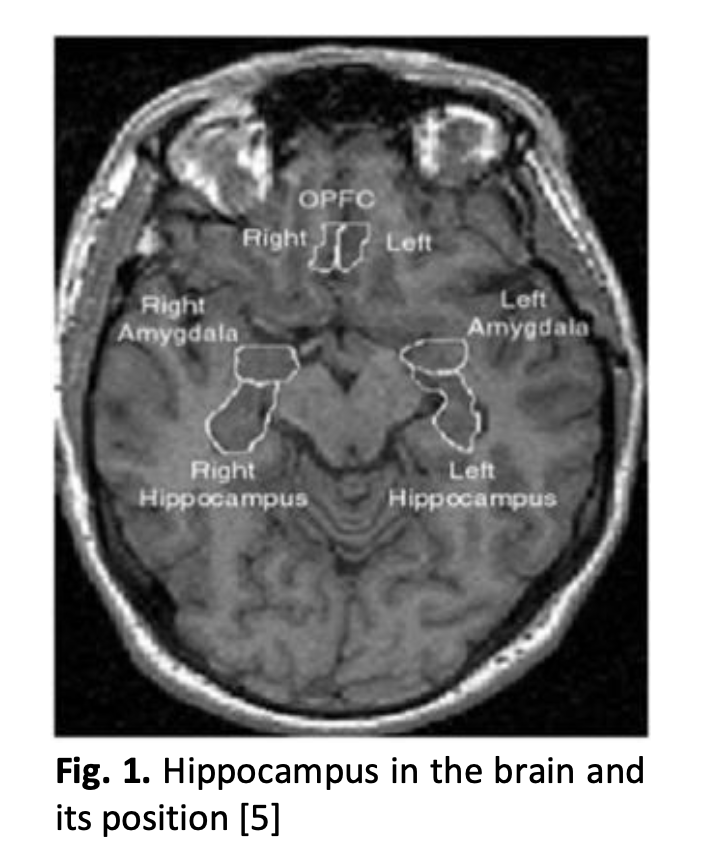
Hippocampus Segmentation of Brain MRI Images for Possible Progression Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.2.234241Keywords:
Alzheimer’s disease, segmentation, MRI, ADNIAbstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) has become as one of the most serious ailments that need to be faced by people all over the world. There is no cure for AD, but the progression of the illness may be reduced with the early detection and proper monitoring of the disease. Many current studies focused more on early detection but does not include the monitoring process as well. Proper monitoring system is as critical as early diagnosis since it allows doctors to assess the disease development of Alzheimer's patients quantitatively. This study proposes to develop an algorithm for detecting the hippocampus of patients with Alzheimer's disease in MRI images and use that for the purpose of progression detection of the disease. After performing some pre-processing steps, the active contour method (Chan-Vese) was used to extract the region of interest (ROI). Next, certain parameters were calculated including the number of pixels and area pixels. From the extracted parameters of the patients from two different MRI sessions, percentage of progression is calculated by measuring the reduction in pixel numbers from those images. This study was able to develop a semi-automated and robust model based on the Chan-Vese segmentation technique, where it could observe the shrinking of the patient brain by the progression method using the total pixels of the hippocampus and its area by getting decreased at the second visit. Based on the result, it shows that this study could be further extended by implementing various feature extraction techniques to come out with a more robust output which can be used for progression detection of Alzheimer’s disease.
Downloads