Comparative Analysis of Housing Cluster Formation on Outdoor Thermal Comfort in Hot-Arid Climate
Keywords:
Housing cluster formation, thermal comfort, hot arid climate, predicted mean voteAbstract
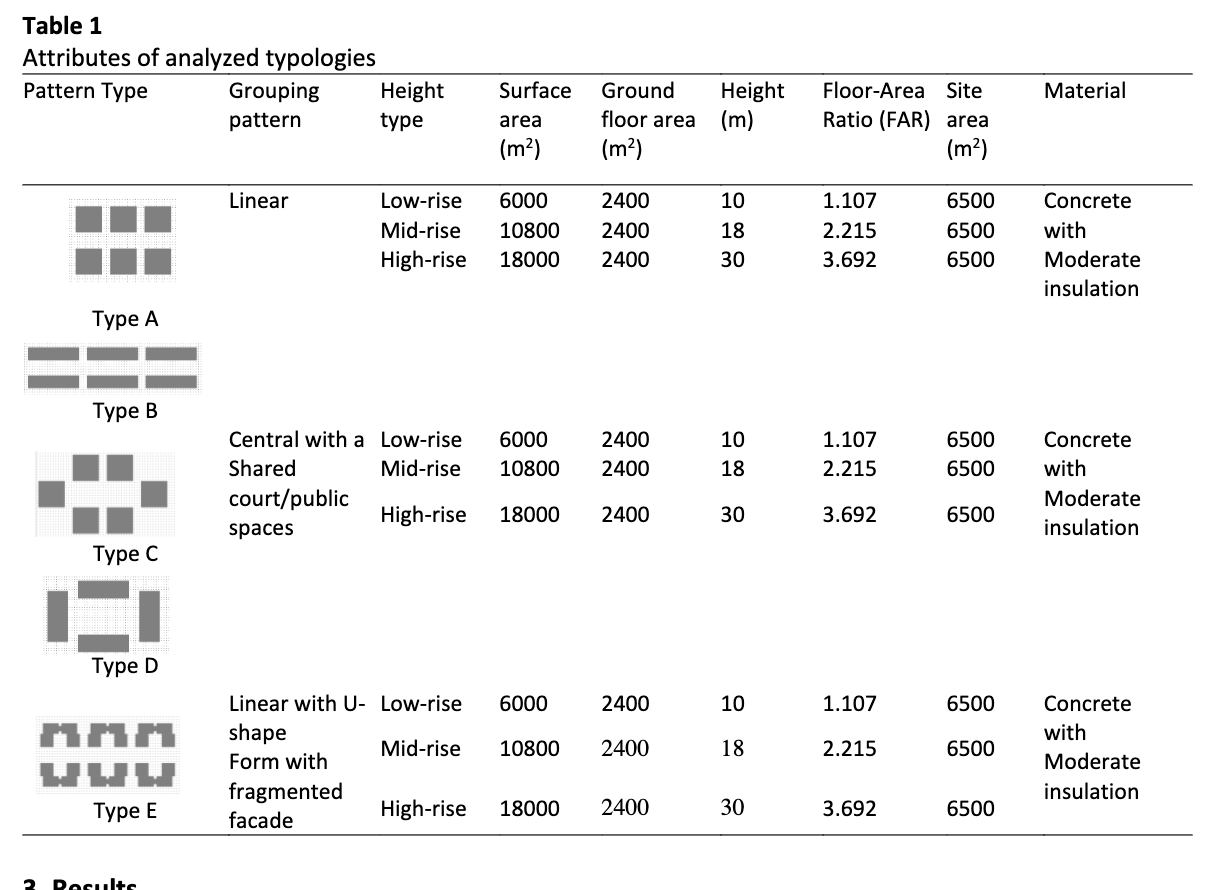
Recent literatures have addressed the effect of building formation on outdoor thermal comfort at urban scale level in various environmental climate contexts. However, there is a research gap in studying the effect of housing clusters formationinspecific climate context for Baghdad city as an example of hot aridclimate, and its effects on the outdoor thermal comfort. This research aims to comparatively analyze and simulate different housing cluster formations in terms of height, contiguity, and grouping of buildings and their effect on outdoor thermal comfort city using ENVI-MET 4.4.2 software. The simulation depends on several parameters analyses that include Predicted Mean Vote (PMV), mean radiant temperature, air temperature, humidity, and airspeed. The results of this research found the optimized building formation which improves microclimate thermal comfort on the pedestrian level for hot aridclimate.
Downloads