Thermally Stratified Flow of Cu-Al2O3/Water Hybrid Nanofluid past a Permeable Stretching/Shrinking Circular Cylinder
Keywords:
Hybrid nanofluid, stretching/shrinking cylinder, suction, thermal stratificationAbstract
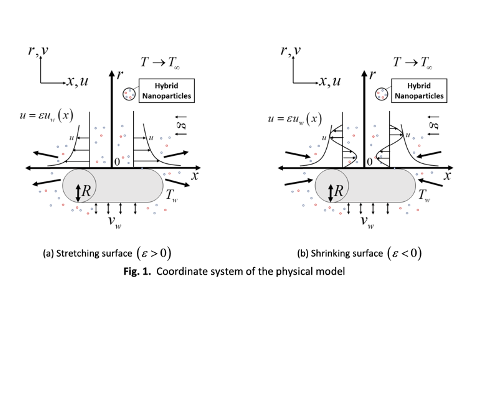
The present study emphasizes the thermally stratified hybrid nanofluid flow due to a permeable stretching/shrinking cylinder. Thermal buoyancy force is also taken into consideration to incorporate with the thermal stratification process. An improved hybrid nanofluid (dual nanoparticles) may offer a better heat transfer performance in many engineering applications. In the present work, the combination of copper (Cu) and alumina (Al2O3) nanoparticles with water as the working fluid is analytically modeled using the extended form of Tiwari and Das nanofluid model. A suitable transformation is adopted to simplify the boundary layer and energy equations into a nonlinear system of ODEs. A boundary value problem solver with fourth order accuracy (bvp4c) in the MATLAB software is utilized to solve the transformed system. The change in velocity and temperature as well as the heat transfer rate and skin friction coefficient are deliberated and graphically manifested for appropriate values of the dimensionless stretching/shrinking, nanoparticles volume fraction, and thermal stratification parameters. The presence of dual solutions is seen on all the profiles within the range of selected parameters.
Downloads