Data Normalization Methods of Hybridized Multi-Stage Feature Selection Classification for 5G Base Station Antenna Health Effect Detection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.30.2.133140Keywords:
5G, radiofrequency electromagnetic field, base stations, normalization method, antenna and propagation, bioelectromagneticsAbstract
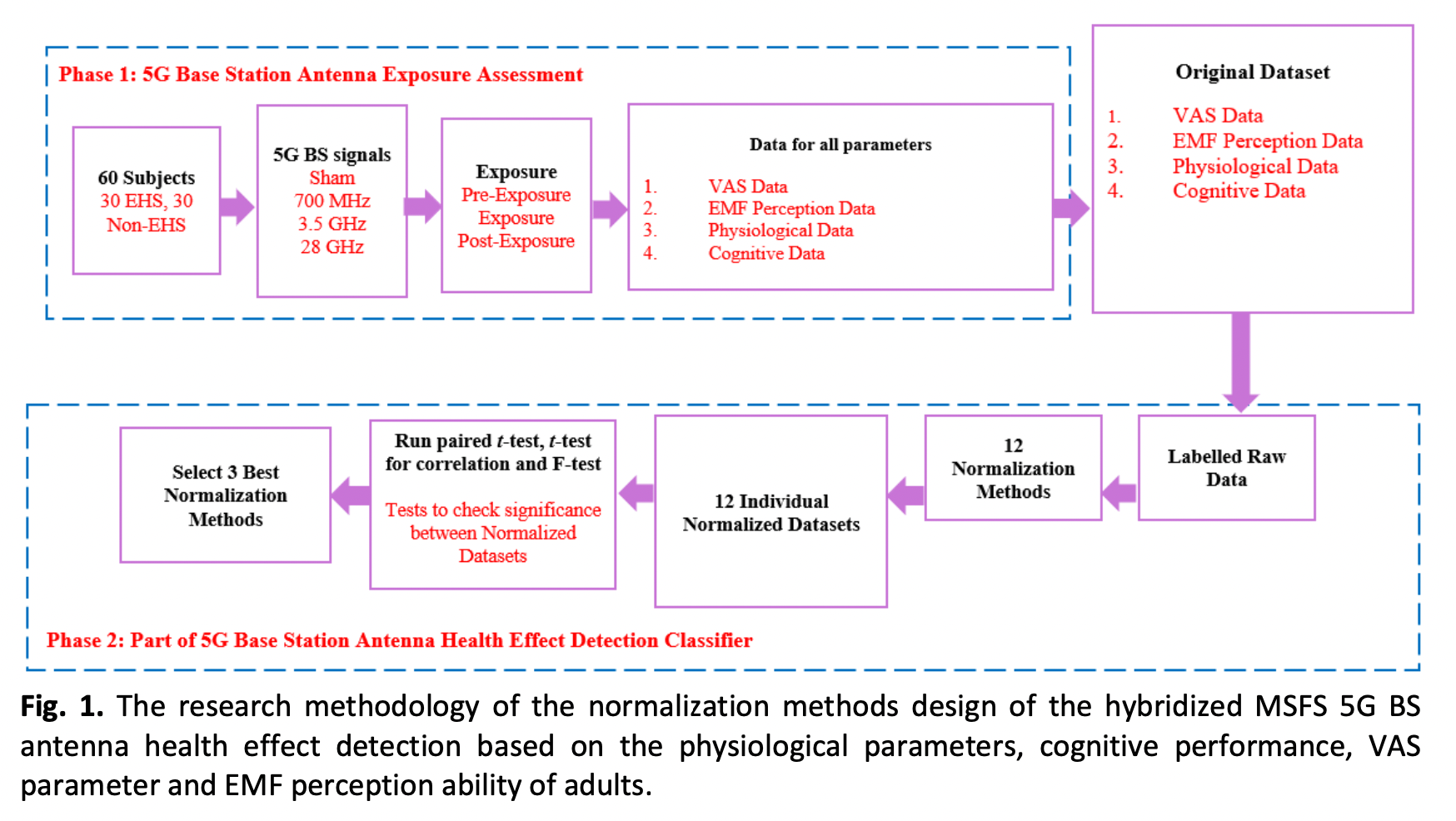
It is essential to assess human exposure to Fifth Generation (5G) Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field (RF-EMF) signal from Base Station (BS) sources operating at Low Band 5G at 700 MHz, Sub-6 Band 5G at 3.5 GHz, and Millimeter Wave (mmWave) 5G at 28 GHz. This assessment will help determine whether 5G technology is safe for people. Inconsistent results were found in previous epidemiological studies on the health effects of radiation exposure from Mobile Phones (MP) and BS when normalization methods were used to prepare the data for Machine Learning (ML), which could lead to misclassification because of the dataset's quality. The effects on adult health are assessed in terms of physiological parameters (body temperature, heart rates, and blood pressure), cognitive performance (brain memory, motor control, and attention), Visual Analogue Scales (VAS) for well-being parameter, and Electromagnetic Field (EMF) perception parameter. The purpose of the research was to identify changes in the physiological parameters of adult individuals before, during, or after exposure to 5G signals, including Sham (No Exposure). 12 normalization methods are selected which are Z-score normalization (z score), Linear scaling (LS), Binary normalization (BNN), Bipolar normalization (BPN), Min-Max scaling (MMS), t-score normalization (t score), Decimal Inverse Logarithmic Scaled Normalization (DILSN), Relative Mean Normalization (RMN), Relative Standard Deviation Normalization (RSDN), Variation Normalization (VN), Robust Normalization (RN) and Relative Interquartile Normalization (RIN) and based on their F-value and p-value analyses, the three best normalization techniques are selected in this research. The original distribution of each parameter data variable is different, these techniques are beneficial for converting data so that it is dimensionless and has equivalent distributions. Based on the selection criteria for the hybridized Multi-Stage Feature Selection (MSFS) classification for 5G base station antenna health effect detection, BNN, MMS, and RSDN were named as the top three normalization techniques.
Downloads