Comparison of Phenolic Compound, Colour Value, and Antioxidant Activity of Roselle Calyces Extract between Modified Supercritical Carbon Dioxide and Conventional Extraction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.29.2.204211Keywords:
Roselle, Modified supercritical carbon dioxide, Phenolic, AntioxidantAbstract
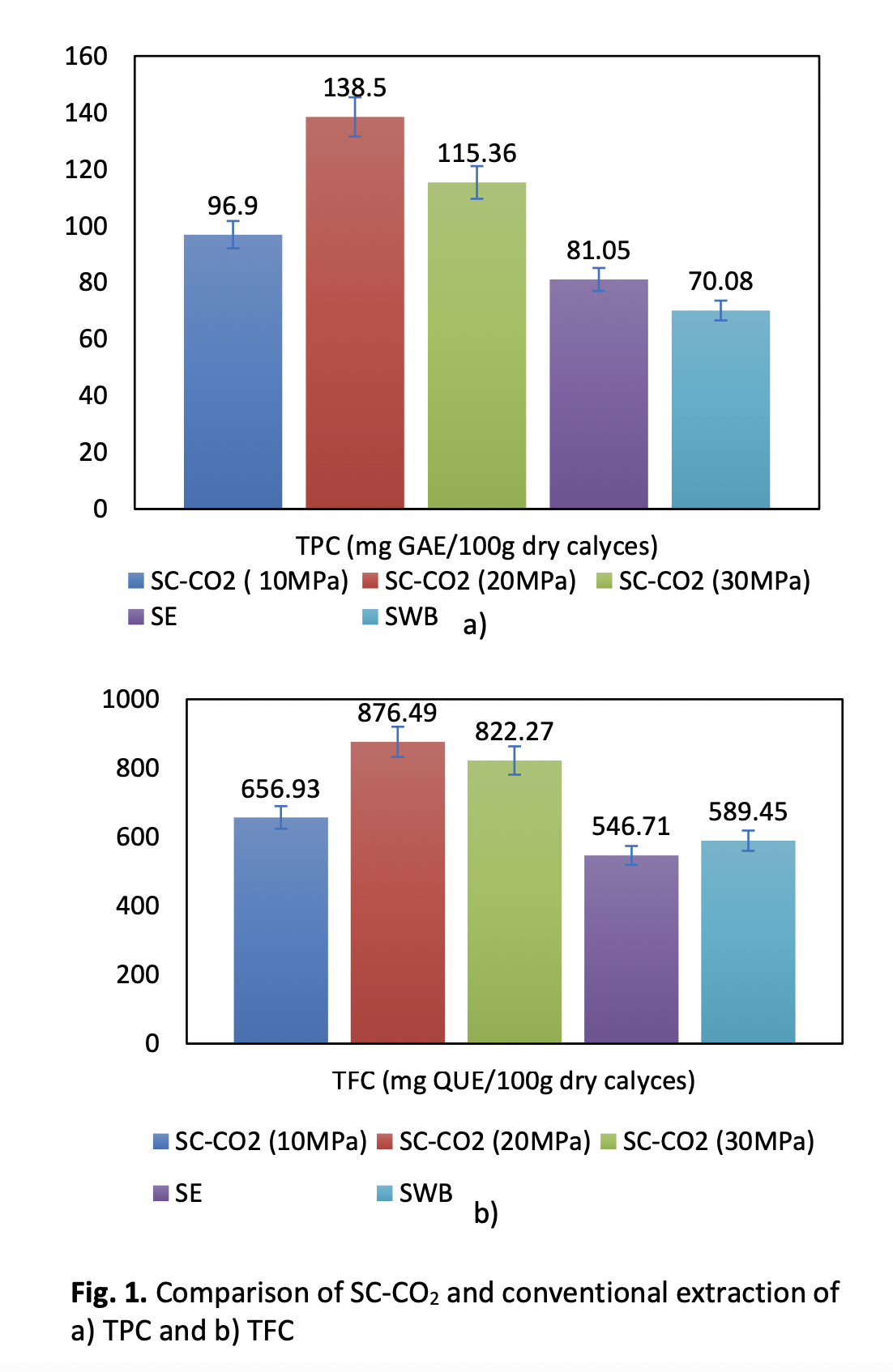
Supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) is a clean and green technology for extracting polyphenols and antioxidants from roselle (Hibiscus Sabdariffa) as nutraceutical ingredients and high-value co-products development. To increase the SC-CO2 fluid affinity towards polar compounds, general regard as a safe (GRAS) solvent, ethanol-water was added in a small amount as a modifier. Dry roselle calyces were extracted using modified SC-CO2 and conventional methods (Soxhlet and Shaking Water Bath) to determine whether the SC-CO2 technology may improve the extraction of phenolic content and antioxidant activity. The results showed that the SC-CO2 extract had a significantly higher yield of total phenolic and flavonoid content than the conventional extraction method. The conventional method produces a redder but lighter extract than SC-CO2 extraction. SC-CO2 also had a higher antioxidant activity as measured by DPPH radical scavenging. These results suggest that SC-CO2 technology increases the quantity and quality of roselle calyces’ extract. The findings increased the reliability of using this technique to produce high-value products from this high-value plant. Roselle as a low-cost sustainable local crop source, as well as SC-CO2 as a clean energy process with low environmental impact, excellent solvent recyclability, and reduced chemical use, could increase the market value of antioxidant-rich extract.
Downloads