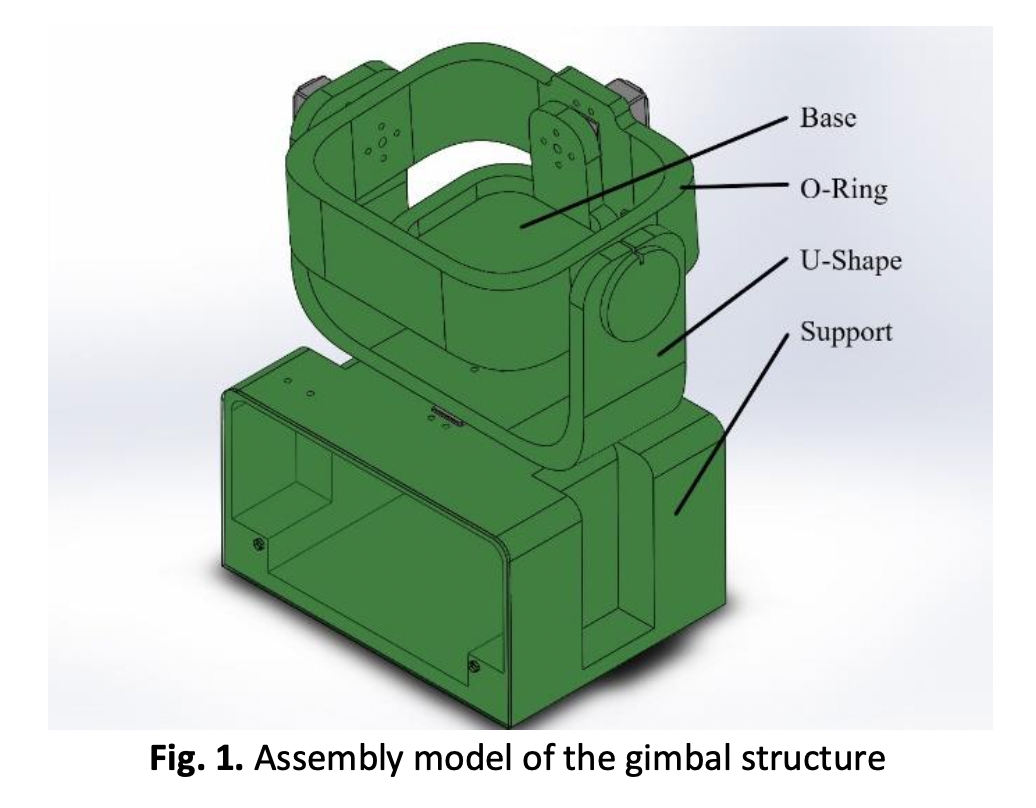
Design and Simulation of a Customize Three-axis Gimbal Structure using Finite Element Analysis Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.30.1.158167Keywords:
Gimbal, Finite element analysis, Computer-Aided Engineering, SolidWorksAbstract
This paper presents a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) on a customized three-axis gimbal design application. Examples of applications of the gimbals such as drones, camera stabilizers, and spacecraft. The SolidWorks software checked the gimbal’s FEA characteristics with no existing load or normal conditions. Using the FEA method, a static simulation analysis where the material of this assembly design uses Polylactic Acid (PLA), used mainly by 3D printer machines. The force is given to the gimbal structure and obtains the results of the maximum value of stress in MPa, displacement in mm, and strain. Thus, based on the results obtained from SolidWorks, the structure will not fail. The maximum stress value between parts is 2.31 MPa for the support part and 3.09 MPa for the assembly model when the yield stress value of the PLA material properties is at 70 MPa. The new design structure for the gimbal hardware focuses on academic purposes based on PLA material and is easy to build using a 3D printer. In the summary, the customized three-axis gimbal design using SolidWorks will not fracture when the design is in normal condition which has a total force of 6.87 N, which is equal to 0.70 kg at 3.09 MPa where the weight of the base, O-ring, and servo motors at the U-shape part. In addition, the design can hold up to 230.87 N, which is equal to 23.54 kg at 69.90 MPa of the stress value before it will fail at 70 MPa.
Downloads