Fabrication of ZnO Nanostructures Doped with Nb at Different Concentration as a Argon Sensor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.31.1.365372Keywords:
ZnO nanoparticles, Nb doped, thermal immersion method, gas sensor, Ag gasAbstract
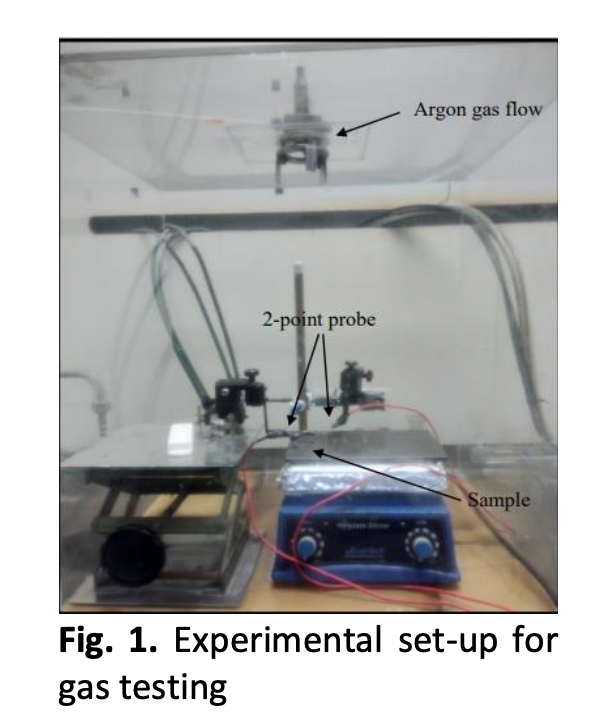
This works presents the report on the study of ZnO nanoparticles doped on silicon substrate. ZnO nanoparticles doped was prepared by using thermal immersion method with varies percentage ratio mass of dopant, Niobium. ZnO nanoparticles was characterized for their morphology by using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), crystalline graphic of material by x-ray diffraction (XRD) and electrical properties by IV measurement. The FESEM results showed that the randomly rougher distribution of ZnO nanoparticles doped with Nb covering on Si surface. XRD results reveals that ZnO nanoparticles doped with Nb was successfully growth on the silicon substrate. IV measurement was measured by 2-point probes. The measurement of the IV was done before and after sample exposed into argon gas. The argon gas was exposed for 10 minutes to indicate the sensitivity of the sample. The result shows that the sample that doped with 10wt% of niobium was the best sample to indicate the performance of the sensor compare to the other sample as observed in the 88.40% response when exposed to Argon gas.