Analytical and Numerical Simulation of Surface Pressure of an Oscillating Wedge at Hypersonic Mach Numbers and Application of Taguchi's Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.30.1.1530Keywords:
Hypersonic, Mach number, Wedge angleAbstract
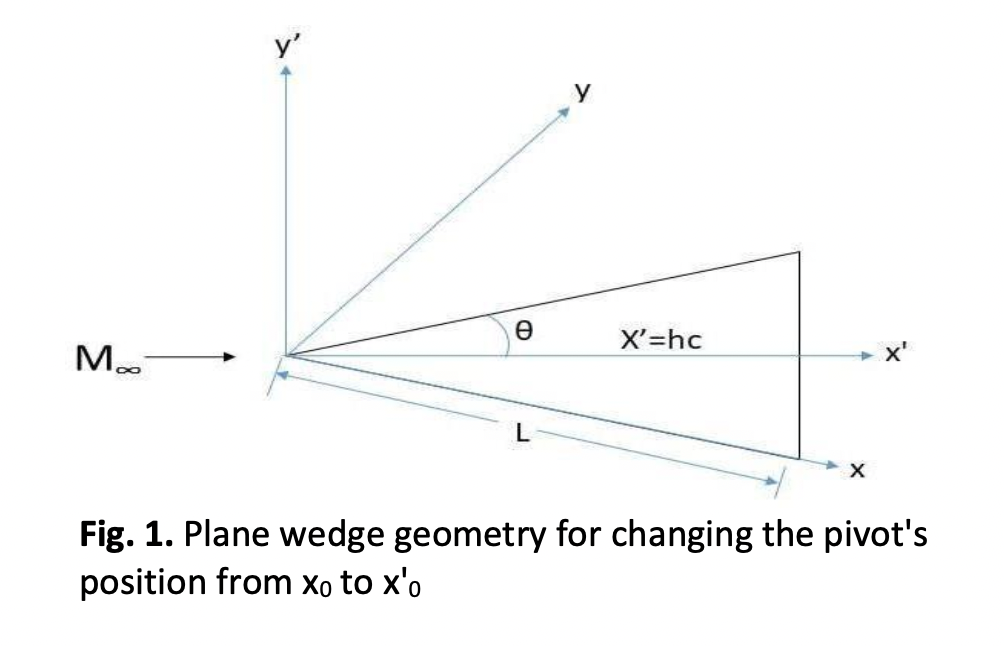
This paper aims to estimate the surface pressure of a wedge at hypersonic Mach numbers at a considerable angle of incidence. The Ghosh similitude, corresponding strip theory, and piston theory are used to determine the pressure distribution analytically, and the results are compared to those of the CFD analysis. The theory is valid when the shock wave is attached to the leading edge of the nose of the wedge. Pressure on the windward surface was considered in the analysis. The pressure on the Lee surface is neglected. The condition for the validity of the theory is that the Mach number M2 behind the shock wave is greater than 2.5. The parameters taken into account for the study are the wedge angle and Mach number. The range of wedge angle considered is from 5 to 25 degrees and the Mach number considered is from 5 to 15. The analytical and the CFD results are in good agreement. The findings indicate that the parameters like wedge angle and Mach number are influential parameters that influence the wedge surface static pressure. The surface static pressure rises with an increase in Mach number and wedge angle.
Downloads