Antibacterial Activity and Inhibition Mechanism of Red Ginger (Zingiber officinale var. rubrum) Ethanol Extract Against Pathogenic Bacteria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.30.1.145157Keywords:
Herbal Medicine, Infection, Pathogen Bacteria, PhytotherapyAbstract
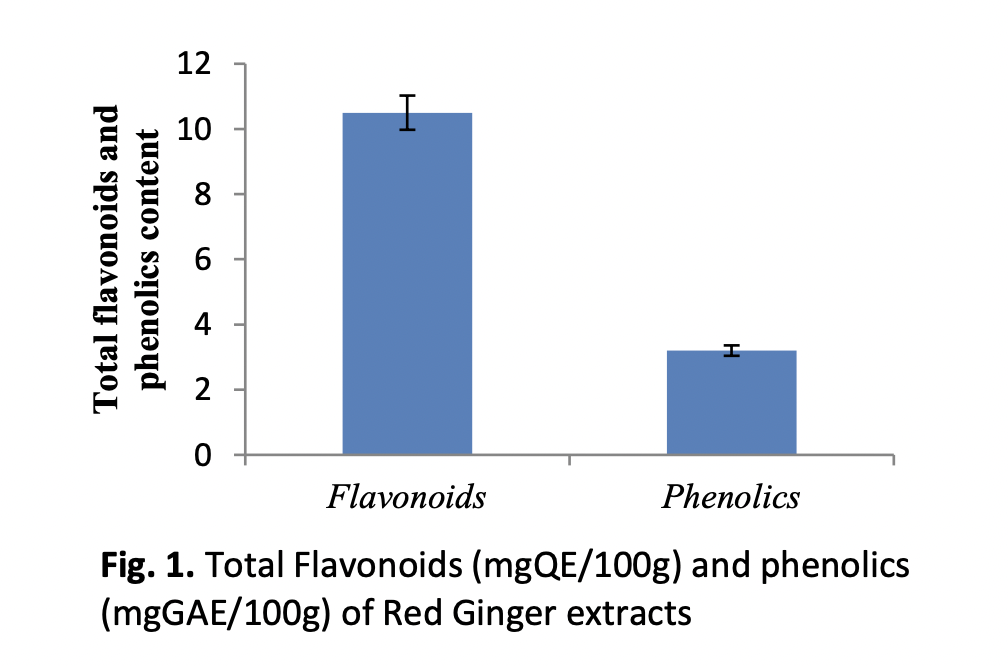
Pathogenic bacteria can interfere with the body health by producing toxic substances, damaging body tissues, multiplying and killing healthy body cells. Therefore, it is crucial to explore safe alternative treatment strategies, such as developing natural bactericidal agents to eradicate infections. Red ginger (Zingiber officinale var. rubrum) has potential as an antibacterial, so it is important to study its activity in inhibiting pathogenic bacteria. The aim of this study was to assess the antibacterial activity and inhibition mechanism of red ginger extract as an inhibitor of pathogenic bacterial infection. Methods such as dilution, Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion, and an inhibition test mechanism using a spectrophotometer and SEM were conducted in this study. Red ginger ethanol extract can inhibit the growth of Salmonela thypi, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Streptococcus mutans at a concentration of 500 µg/mL, while Pseudomonas aeruginosa at a concentration of 250 µg/mL. Further observation of bacterial cell leakage showed that the higher the red ginger ethanol extract concentration, the higher the bacterial cell leakage. Based on SEM results, the quantity of S. thypi, S. epidermidis, and S. mutans after treatment with red ginger ethanol extract decreased, and the cell wall became wrinkled and destroyed. The ethanol extract of the red ginger rhizome can be recommended as a future antibacterial agent, especially for infections caused by pathogenic bacteria.
Downloads