A Hybrid Personalized Text Simplification Framework Leveraging the Deep Learning-based Transformer Model for Dyslexic Students
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.34.1.299313Keywords:
Deep learning, dyslexia, hybrid, personalized text simplification, Transformer modelAbstract
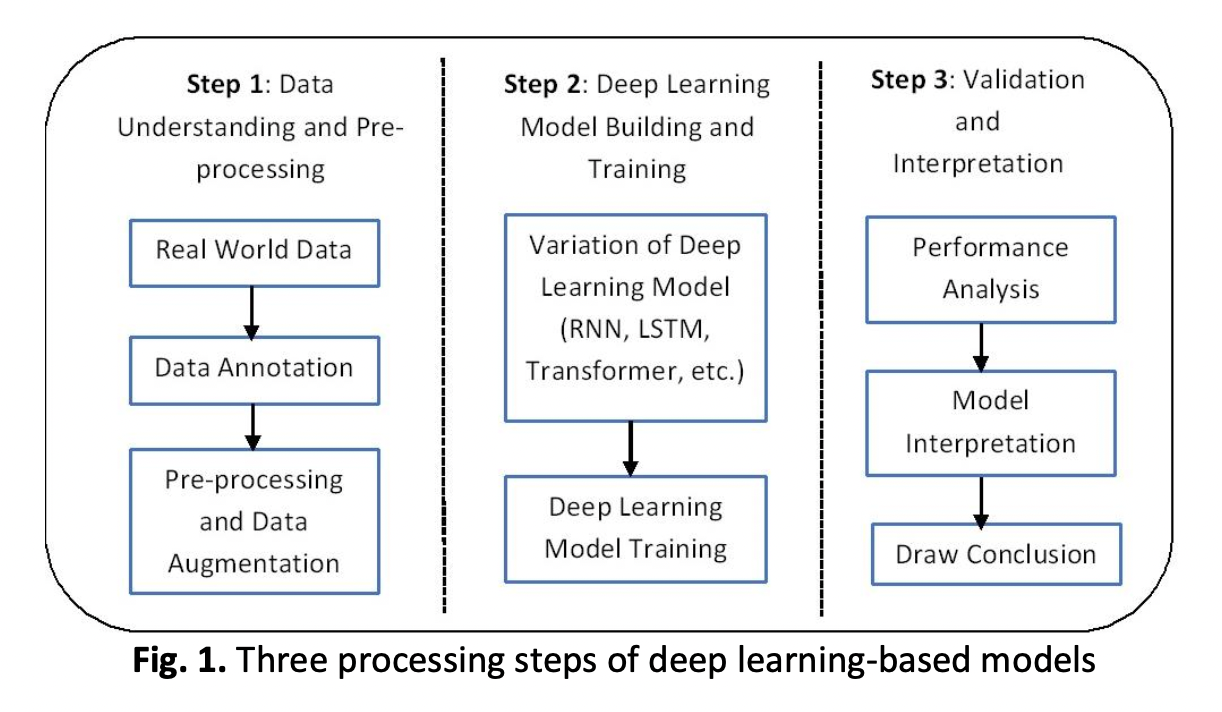
This study proposes a hybrid personalized text simplification framework leveraging the deep learning-based Transformer model to generate simplified expository texts by addressing all sentence perspectives: semantic, syntactic, and lexical. This study targets dyslexic students due to its increasing population in the education context. Dyslexia is a learning disability characterized by reading deficiency and cognitive weakness. Thus, they need a more personalized learning experience i.e., personalized text simplification to support their classroom learning. Unfortunately, the current models of personalized text simplification can only address the syntactic and lexical perspectives of sentences, ignoring the semantic perspective. Other models employed text complexity classification at the beginning of the text simplification workflow with the intention to address the personalization element. Still, no mapping to the deficiencies of its intended users was made, and the semantic perspective of sentences remains under study. Therefore, this study is conducted to introduce hybrid methods to enhance the current personalization elements, as well as to accommodate generation of simplified expository texts at all sentence perspectives. An extensive literature was conducted using established online databases. The proposed hybrid framework is further divided into three distinct phases: Phase 1) two-phase personalization, Phase 2) multi-label text complexity classification, and Phase 3) explicit editing. It is expected that a successful implementation of the proposed hybrid personalized text simplification framework can accelerate the learning motivations of dyslexic students, hence increasing their academic achievements and reducing academic dropout rates.
Downloads