Visualising Current Research Trends in Class Imbalance using Clustering Approach: A Bibliometrics Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.38.2.95111Keywords:
Imbalance problem, clustering approach, network analysis, science mapping, big dataAbstract
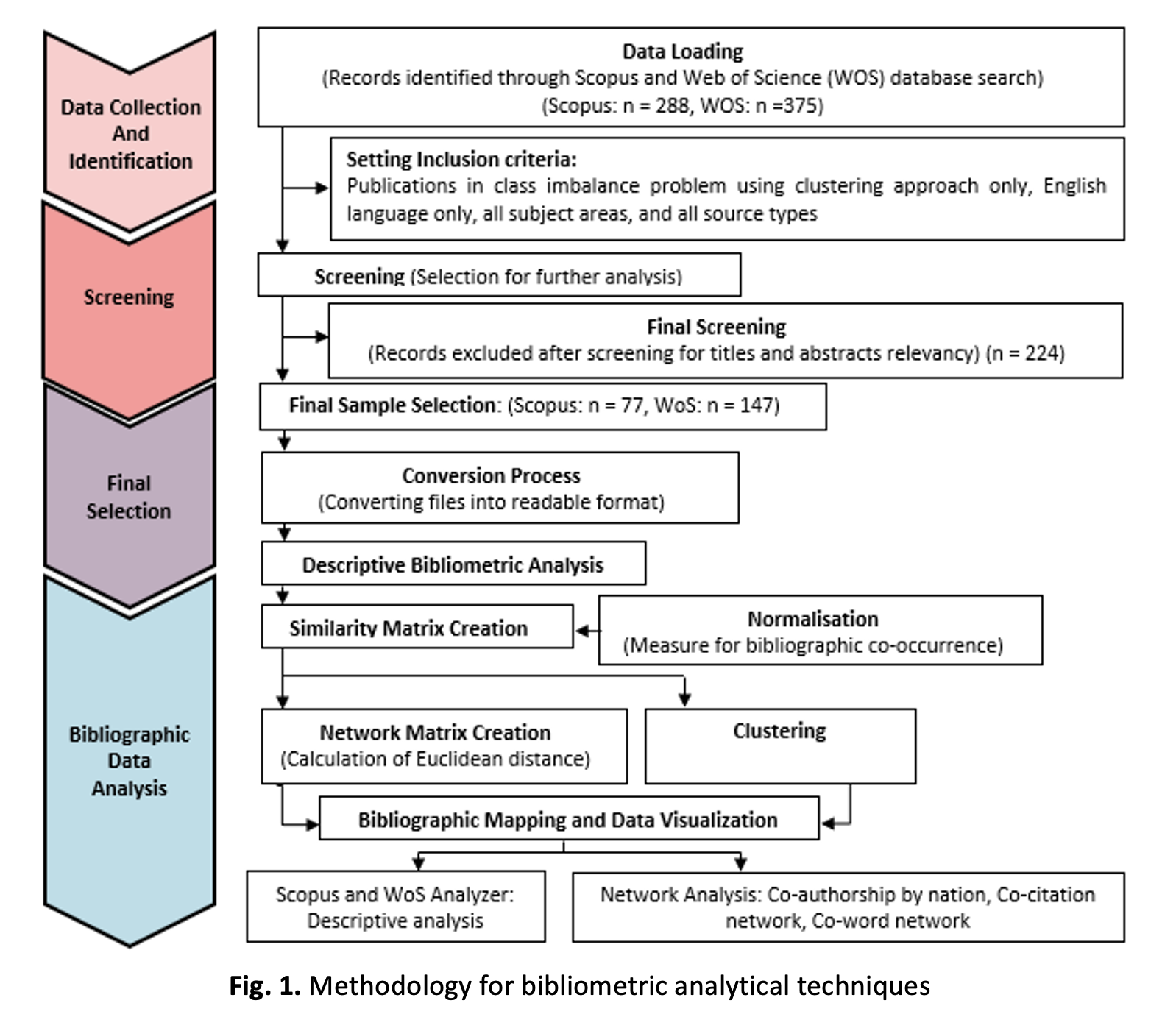
In recent years, extensive research has been carried out on big data class imbalance problems using the clustering approach. The bibliometric analysis employs statistical techniques to map and assess trends in a specific research domain based on keywords, author affiliations, and citations. Bibliographic analysis assists us in comprehending unstructured big data. This study aims to present a comprehensive literature review on class imbalance problems using the clustering approach and identify gaps in the research domain using bibliometric analytical techniques. The Scopus and Web of Science databases were used to extract 663 articles on class imbalance data using a clustering approach published between 2010 and 2021. We used the VOS (Visualisation of Similarities) viewer to visualise the bibliometric analytical outcomes. Co-citation and co-word analysis were used to visualise the publication trend and identify areas of current research interest. The study's key findings evidenced a growing interest in the research domain. Herrera, f., and Chawla N. V. are dominant authors in this field, and China is leading the publication in the clustering approach for the big data imbalance problem. The top three affiliations are from China: Tsinghua University, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Beihang University. Conducting an in-depth bibliometric analysis using other databases such as Science Direct, IEEE, and Emerald is recommended. This study may assist researchers in understanding the nature of the big data imbalance problem using a clustering approach and providing insights for future research derived from these worldwide databases.
Downloads