Team Formation for Agile Software Development - Crowdsourcing-based Empirical Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.34.2.133143Keywords:
Agile Software Development, team formation, team composition, empirical, crowdsourcing-based empirical studyAbstract
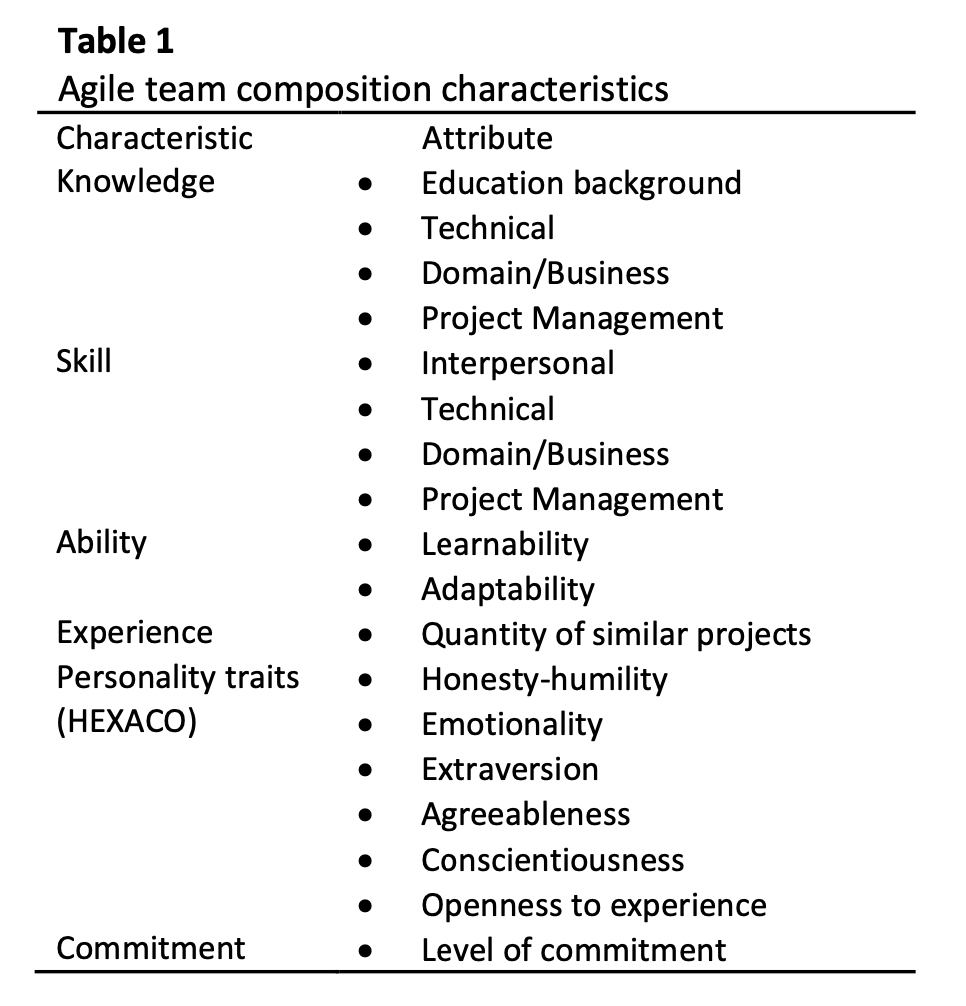
Agile Software Development (ASD) is gradually substituting the plan-driven Waterfall development process. The nature of ASD requires that Agile development teams be more effective than any other development team in that Agile development is incremental, rapid, and responds well to changes. Therefore, team formation should be done properly in order for effective teamwork which leads to great performance and project success. To date, there is limited guidance, model, or frameworks that can assist in achieving optimum team formation. Currently, team formation is done based on heuristics and instincts which seemingly results in bias and incorrectness. This study aims to validate the Agile team formation conceptual model. This paper reports the initial empirical study that was done using a crowdsourcing-based method due to pandemic restrictions on close contact. The study was done in an Agile professional network group platform on the internet. The data collected is then analysed using contents analysis. The respondents validated that the team formation characteristics in the conceptual model were applicable with an emphasis on continuous learning and having a growth mindset. Future plan would be to determine the optimized team formation by using elements of Artificial Intelligence algorithms such as Genetic Algorithm.
Downloads