Influence of Process Variables on Density of Aluminium Chip-Base Feedstock Prepared For Non-Melted Hot Extrusion Recycling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.33.2.351359Keywords:
Annealing, non-melted recycling, aluminium chip, ANOVAAbstract
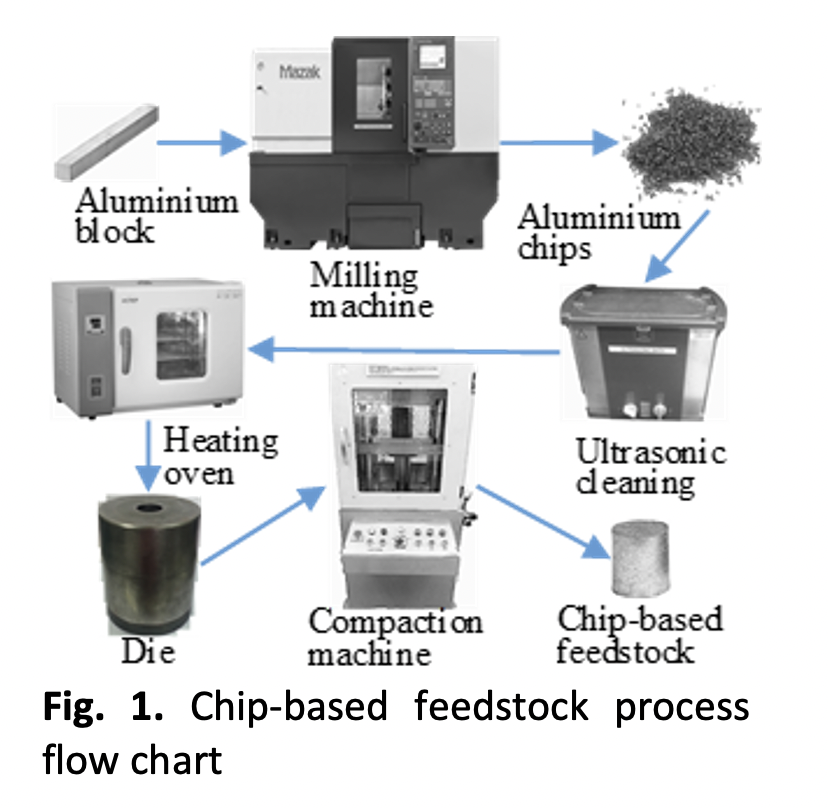
Non-melted recycling of aluminium chips via hot extrusion is an alternative technique towards sustainable manufacturing. The process prior to hot extrusion is crucial in achieving free-microvoid extrudates, which were caused by air trapped in chip-based feedstocks. In this work, heat treatment was performed on the chips before they were compacted into the feedstock. The effect of annealing temperature, time and compaction pressure on density was investigated. The experiment is conducted using a 23 factorial design, and an ANOVA is used to identify the main parameters. Upon compaction, feedstocks were visually inspected and tested. The results indicate that parameters such as compaction pressure, annealing temperature, and annealing time are statistically significant. The main parameter is the compaction pressure, followed by the annealing temperature, the interaction between the annealing temperature and the annealing time, and the annealing time. At high annealing temperatures, annealing time does not have a significant effect on density. However, at low annealing temperatures, annealing time plays a significant role. Feedstock made from the non-annealed chips has lower relative density compared to annealed chips. Furthermore, the higher the density of the feedstock, the fewer voids will appear on the surface of the product.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2023-11-09
Issue
Section
Articles



























