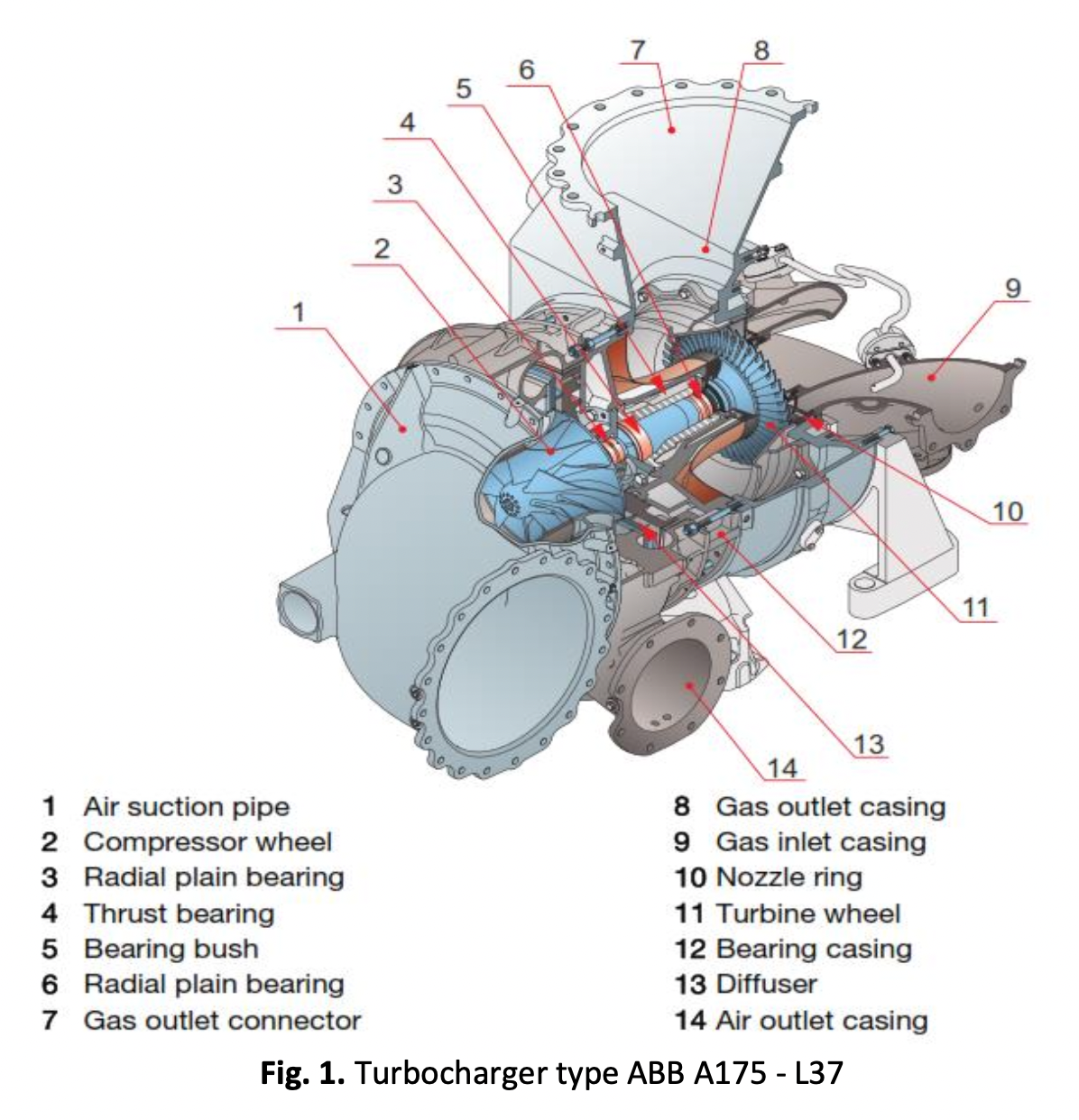
Performance Analysis of Wartsilä Turbocharger W18V50SG at Gas Engine Power Plant Sumbagut-2 Peaker 250 MW
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.1.169178Keywords:
Combustion exhaust gas, combustion chamber cylinder, Otto cycleAbstract
A turbocharger is a device that uses the energy in the exhaust gas produced during combustion to increase the amount of air intake that goes into the cylinder. At gas engine power plant SUMBAGUT 2 PEAKER 250 MW, the use of a turbocharger is thought to be efficient because it can recycle combustion exhaust gases, whose pressure and temperature are still high, to rotate the turbine on the turbocharger. As a result, the compressor forcibly suctions air and delivers it to the combustion chamber cylinder because one requirement for good combustion results is that the air must be in a solid state. Thermal efficiency is another way to assess the efficacy of the gas generator engine's performance. With these conditions, a study was conducted with the goal of determining the working system on the turbocharger and calculating the efficiency of the Otto cycle with a compression ratio = 12 (maximum for the Otto cycle), at a peak load of 18,445 kW, engine speed of 500 rpm, ambient temperature (T 1) = 27° C, the mass flow rate of fuel (m _fuel) = 2814 kg/h 0.781 kg/s, then the thermal.
Downloads