The Performance of Papaya Leaf Extract on The Corrosion Rate of Carbon Steel in 0.5 M HCl Solution
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.34.3.3744Keywords:
Papaya leaf, extract, corrosion, inhibitor, carbon steelAbstract
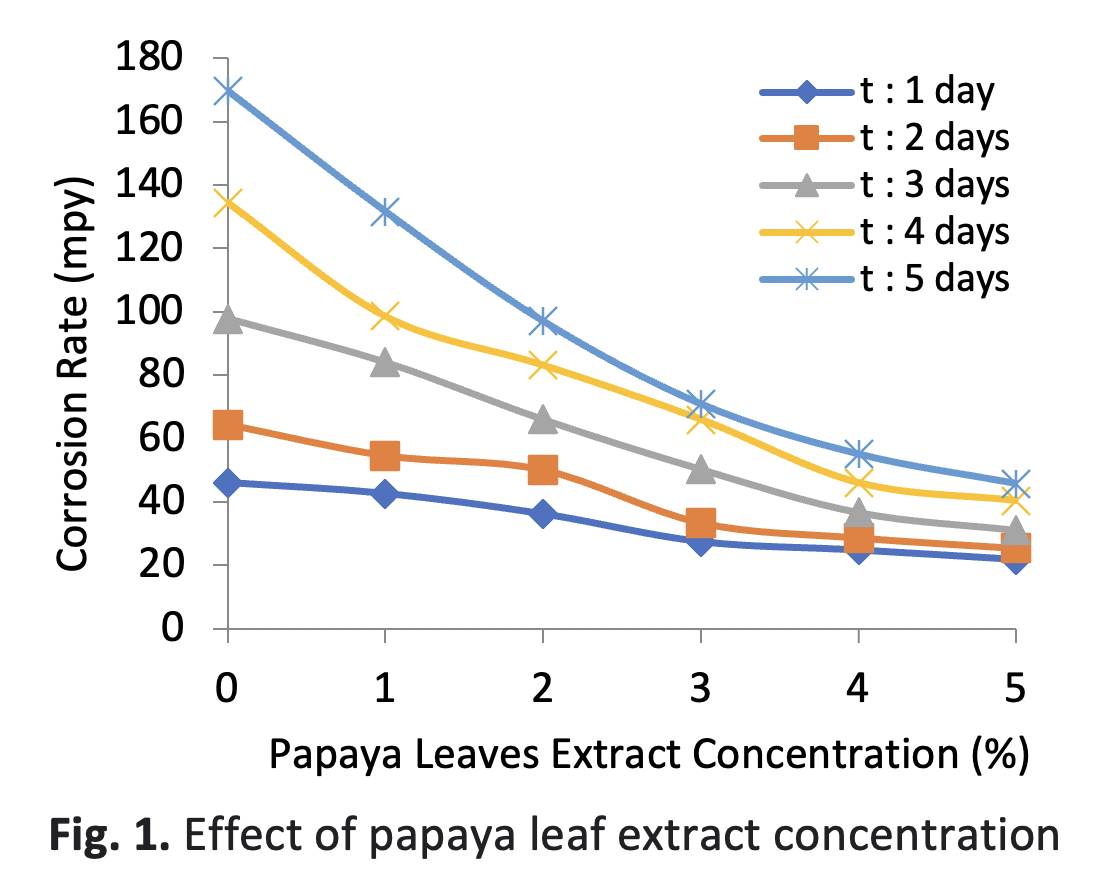
The performance of papaya leaf extract as a corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel metal in 0,5 M HCl solution was investigated using immersion methods. The measurements were conducted in different concentrations of papaya leaf extract and immersion time. It also investigated the effect of temperature on the corrosion rate of carbon steel without and with the use of papaya leaf extract. It would enhance the corrosion inhibitor regarding these materials since the study is still rarely elaborated. The experiments were conducted using ASTM G-31-72 standard practice for laboratory immersion corrosion testing. The carbon steel corrosion rate and inhibition efficiency were examined. Results show that the concentration of papaya leaf extracts influences the corrosion rate of carbon steel. Higher papaya leaf extract concentration reduces the carbon steel corrosion rate. The increasing immersion time increases the corrosion rate. Moreover, increasing temperatures increase the corrosion rate. The inhibition efficiency increases with the increase of papaya leaf extract concentration. The highest inhibition efficiency is 73.10% which reached a concentration of 5% and immersion times of 5 days.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.