FDM Parameters Optimization for Improving Tensile Strength using Response Surface Methodology and Particle Swarm Optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.38.2.112128Keywords:
Additive Manufacturing (AM), Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), Particle Swarm Optimisation (PSO), Response Surface Methodology (RSM), tensile strengthAbstract
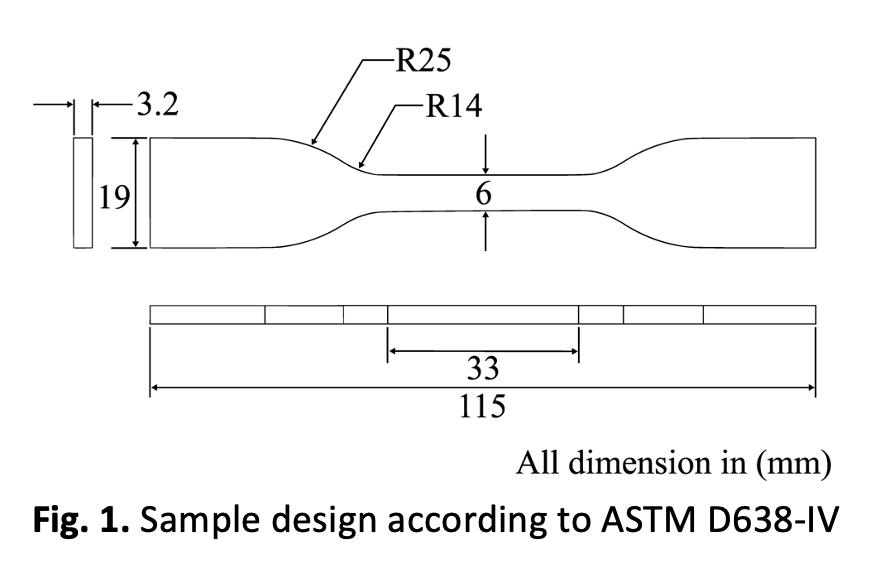
Fused deposition modelling (FDM) is a popular 3D printing technique that uses a thermoplastic filament as the build material. In FDM 3D printing, tensile strength can be an issue because the layers of the object are built on top of each other, and if the layers do not adhere properly, the object can be weak and prone to breaking. Typically, this problem is caused by incorrect parameter settings. Hence, this study was then carried out to analyse and improve the printing quality in term of tensile strength of the printed part using the response surface methodology (RSM) and the particle swarm optimization (PSO) method. The effect of four input parameters such as layer height, printing speed, infill density, and print temperature was examined on the tensile strength of polylactic acid (PLA) standard samples ASTM D638-IV. The experimental design was performed using face-centred central composite designs (FCCD). The experimental data were statistically analysed to form a regression model of the tensile strength. This model was used to approximate the actual process. The optimization was performed using desirability analysis from RSM and PSO to search for the optimal parameter for maximum tensile strength. Experimental results showed that PSO outperformed RSM with a 1.52 % reduction in tensile strength. The maximum tensile strength obtained from PSO was about 39.069 MPa with the optimal process parameters of layer height of 0.30 mm, printing speed of 30.17 m/s, infill density of 79.72 %, and print temperature of 205.92 °C.
Downloads