An Evaluation of Fuzzy in Image Enhancement: Design and Comparison for Penicillium and Aspergillus Species
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.38.2.2744Keywords:
Fuzzy-partition gamma adaptive histogram equalization (FpGAHE), surrounding neighborhood, nearest neighbor, image enhancement, image classificationAbstract
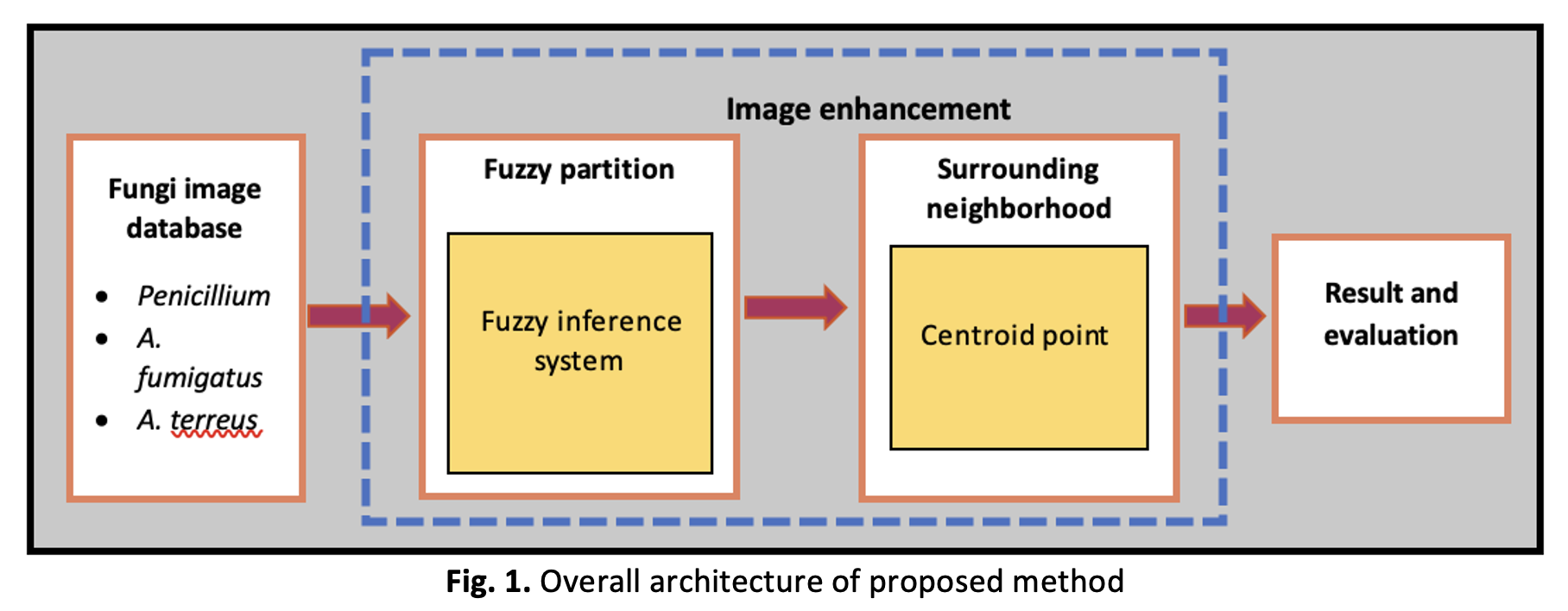
The main focus in this study is to enhance and classify the image of a type of filamentous fungi named Penicillium and Aspergillus. For image enhancement, fuzzy-partition gamma adaptive histogram equalization (FpGAHE) is proposed to improve the quality of an image, in particular the low quality of a microscopic image. Two stages have been considered in this technique. In the first stage, a fuzzy partition is developed to handle the inconsistency of the gray level values of the images by introducing a fuzzy set. In the second stage, surrounding neighborhood is employed to avoid the imbalance data and reduce the drastically changes of brightness values of the image. The performances are evaluated into two parts i.e., image processing and image classification by using the collected microscopic images of fungi species. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed technique, the existing techniques, AHE and AGC is compared to the FpGAHE. In image processing, the result attained shows that the proposed technique has a better performance by obtaining the highest value for the PSNR, SSIM and FSIM evaluation for the species of A. terreus in clean condition. Meanwhile, in image classification, five different nearest neighbor classifiers have been tested. The results show the proposed FpGAHE with Improved Fuzzy-Based k Nearest Centroid Neighbor (IFkNCN) classifier perform the best result compare to other nearest neighbor classifier by obtaining the value of 92.59 and 93.95 for the salt and pepper and Gaussian noise corrupted images respectively.
Downloads