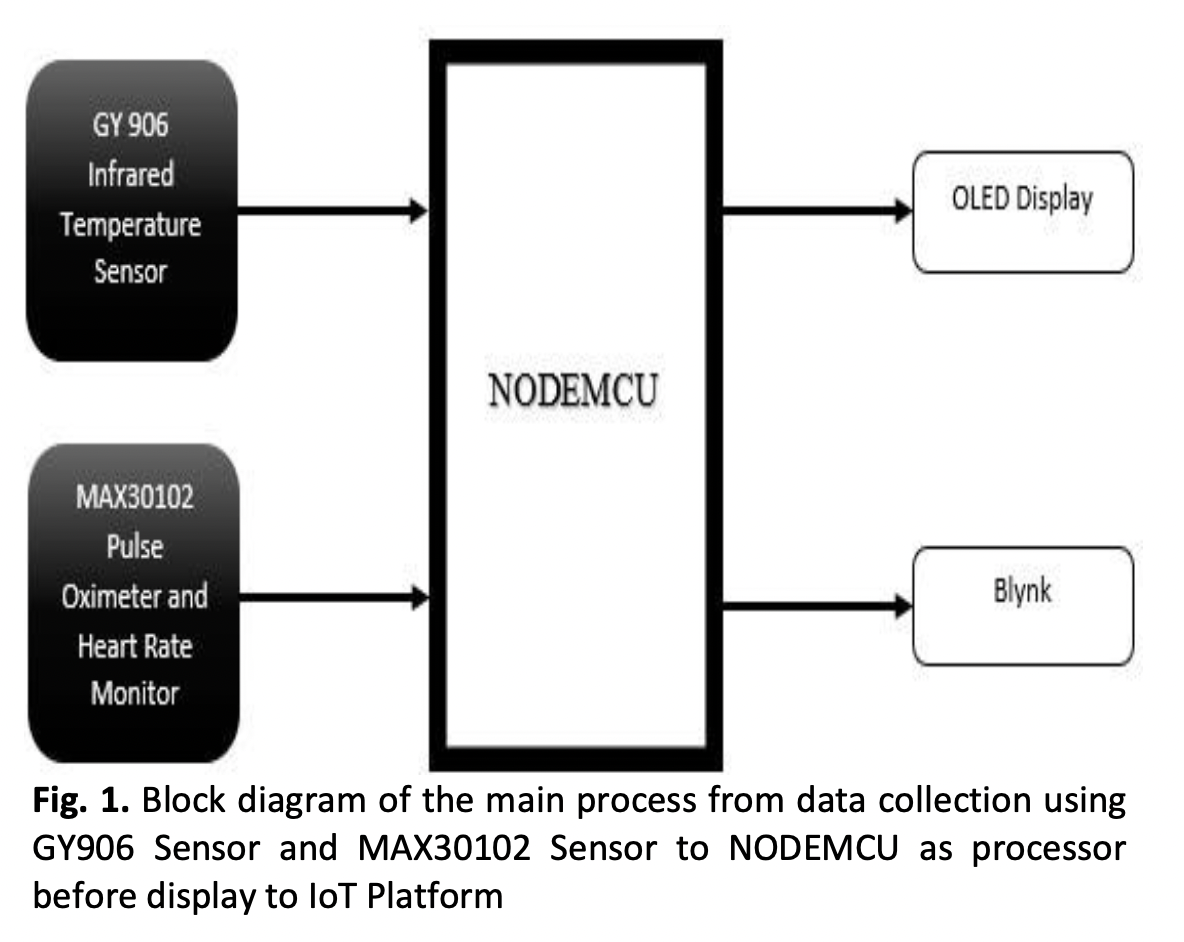
A Framework Study on a Real-Time Operated System for Emergency Medical Services (EMS) using NODEMCU Processor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.33.2.8597Keywords:
Emergency Medical Services, Healthcare Monitoring, Mobility Solutions, Internet of Things, NodeMCUAbstract
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) has always been a great help in treating patients before they arrive at the hospital. On the route to the hospital, where they will receive proper and additional treatment, pre-hospital care is an emergency aid to help stabilise the patient's condition. However, there is a lack of effective maintenance in the data interchange between the emergency department doctors and the paramedics in the ambulance. To give the patient the highest level of treatment, the patient's handoffs from paramedics or pre-hospital to in-hospital staff are not of sufficient quality. Hence came the idea of incorporating the Internet of Things into the emergency healthcare system. This paper discusses a proposed idea to design a reliable healthcare monitoring system that enables data exchange between doctors and paramedics efficiently. This system utilises the IoT platform, Blynk App, to display the data in both places (ambulance and emergency department) by using NodeMCU as the core processor and wearable sensors to measure the main parameters and vital sign data (as is current practise in ambulances). This system may also confirm that data from the sensors is transmitted in real-time to the host computer. The findings indicate that the vital sign readings are roughly accurate when compared to actual devices or marketable measurement tools. At the same time, the system will help the paramedics and doctors communicate efficiently in two ways and enable them to exchange patient details in real-time, so appropriate action can be discussed and the patient can be treated swiftly. The provided information allows hospital professionals in the emergency department to suggest what tools or medications should be ready to treat the patient further.
Downloads