Evaluation of Sick Building Syndrome (SBS) Symptoms and Measurement of Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Parameter in One of Hospital Building in Johor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.52.2.139147Keywords:
Indoor air quality (IAQ), Duct, Airborne, ContaminantAbstract
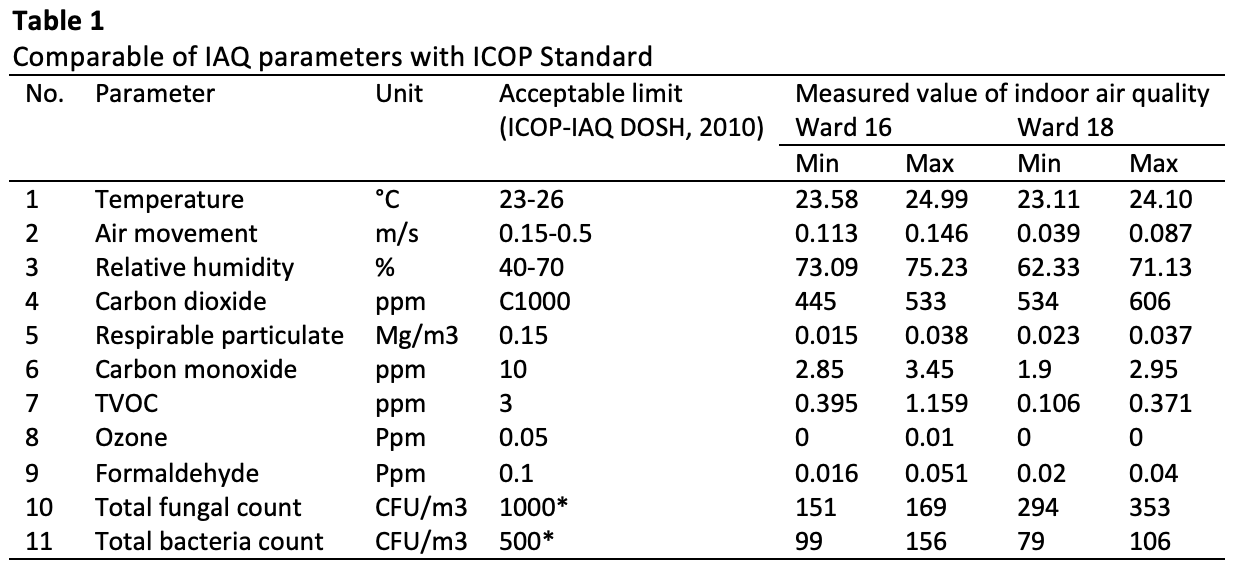
This study assesses Sick Building Syndrome (SBS) symptoms and Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) parameters among hospital ward staff. Utilizing a thorough methodology, a questionnaire survey and IAQ monitoring were conducted, aligning with Department of Occupational Safety and Health (DOSH) guidelines. IAQ parameters are generally within limits, except for relative humidity which recorded values of 73.09-75.23% for Ward 16 and 62.33-71.13% for Ward 18. Respondents expressed concerns about room conditions, including temperature variations, unpleasant odours, and noise. Fatigue, difficulties concentrating, and various respiratory symptoms were prevalent, suggesting potential health issues linked to indoor pollutants. The findings underscore the urgency of addressing IAQ concerns to improve the well-being of patients and healthcare workers.
Downloads