Efficient Classification of Kidney Disease Detection using Heterogeneous Modified Artificial Neural Network and Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.31.3.112Keywords:
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), Machine Learning Technology, Retinal Fundus Image, HMANN (Heterogeneous Improved Artificial Neural Network), Super Fly Optimisation Algorithm (FFOA)Abstract
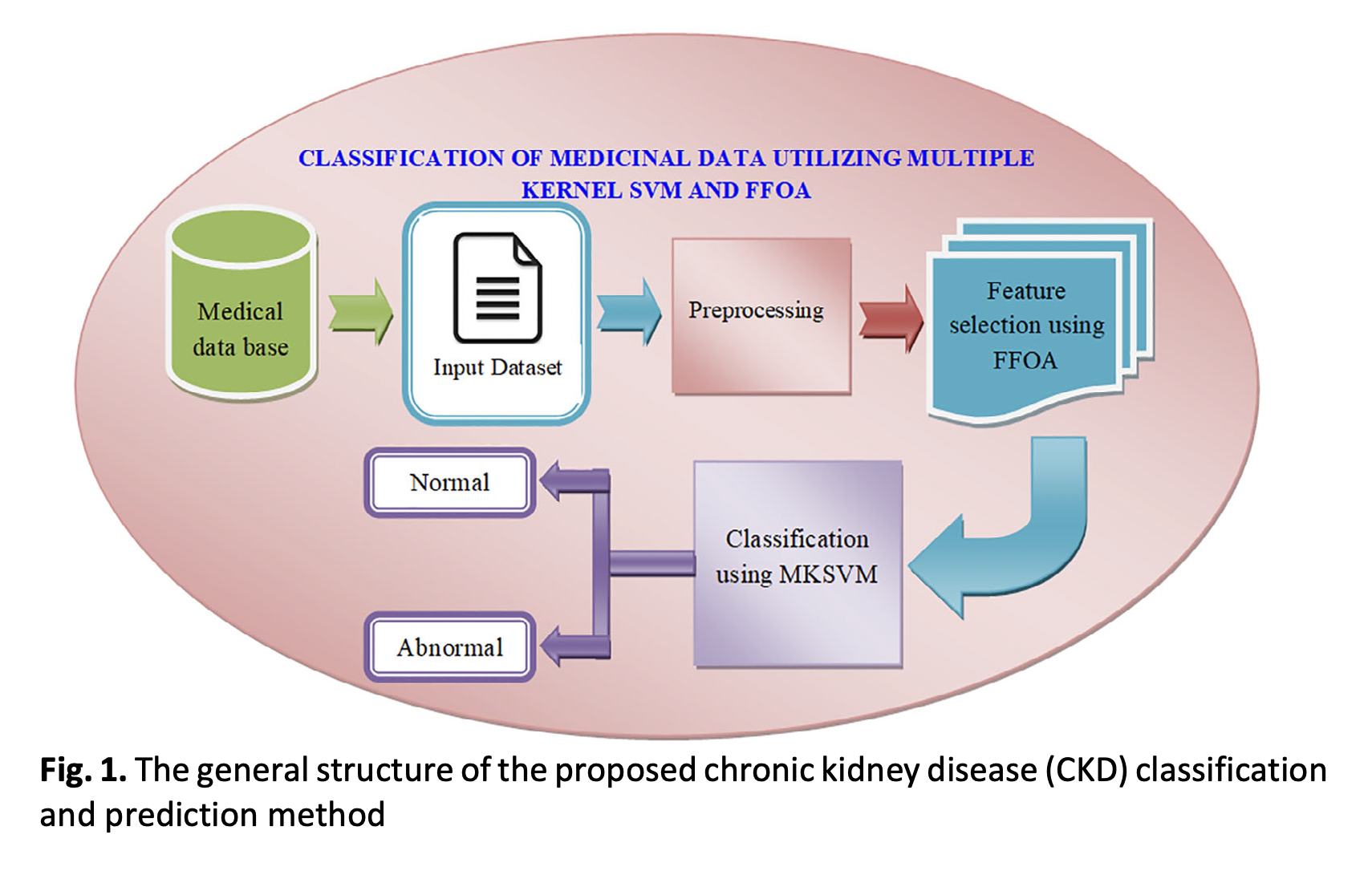
Chronic kidney disease (CKD), a significant issue for public health, affects millions of individuals globally. The course of end-stage renal disease must be stopped or reversed, hence it is crucial to find chronic kidney disease early in order to receive therapy. Prediction of CKD is a second source of treatment, as machine learning techniques, with their high classification accuracy, are becoming increasingly significant in medical diagnosis. To learn about CKD and associated issues in this situation, deep learning is used. The sole inputs used to construct the three distinct types of models were the retinal fundus image alone (test model), the covariate only (the reference model), and the retinal fundus image plus covariate (hybrid model). To maintain the accuracy of contemporary classification systems, feature selection techniques must be applied correctly in order to reduce data size. Here, recommend the Fruit fly optimisation algorithm (FFOA) and the heterogeneous artificial neural network (HMANN) in this paper for efficient disease categorization. An Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) platform is presented for the early detection, segmentation, and diagnosis of chronic renal failure using a heterogeneous modified artificial neural network (HMANN). The Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithms are used to classify the suggested HMANN. The ideal feature is chosen using an FFOA from a large pool of candidate features. The proposed method uses ultrasound pictures as its foundation and, as a first step in processing, slices a region of interest in the kidney in the ultrasound image. The accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive power, negative predictive power, false positive rate, and false negative rate of the suggested CKD classification system were all taken into consideration when evaluating its performance.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2023-08-04
Issue
Section
Articles



























