Predicting the Intention to Use Mobile Health Applications Among Young Adults in Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.37.2.4857Keywords:
Mobile health applications, young adults, UTAUT theory, mobile devicesAbstract
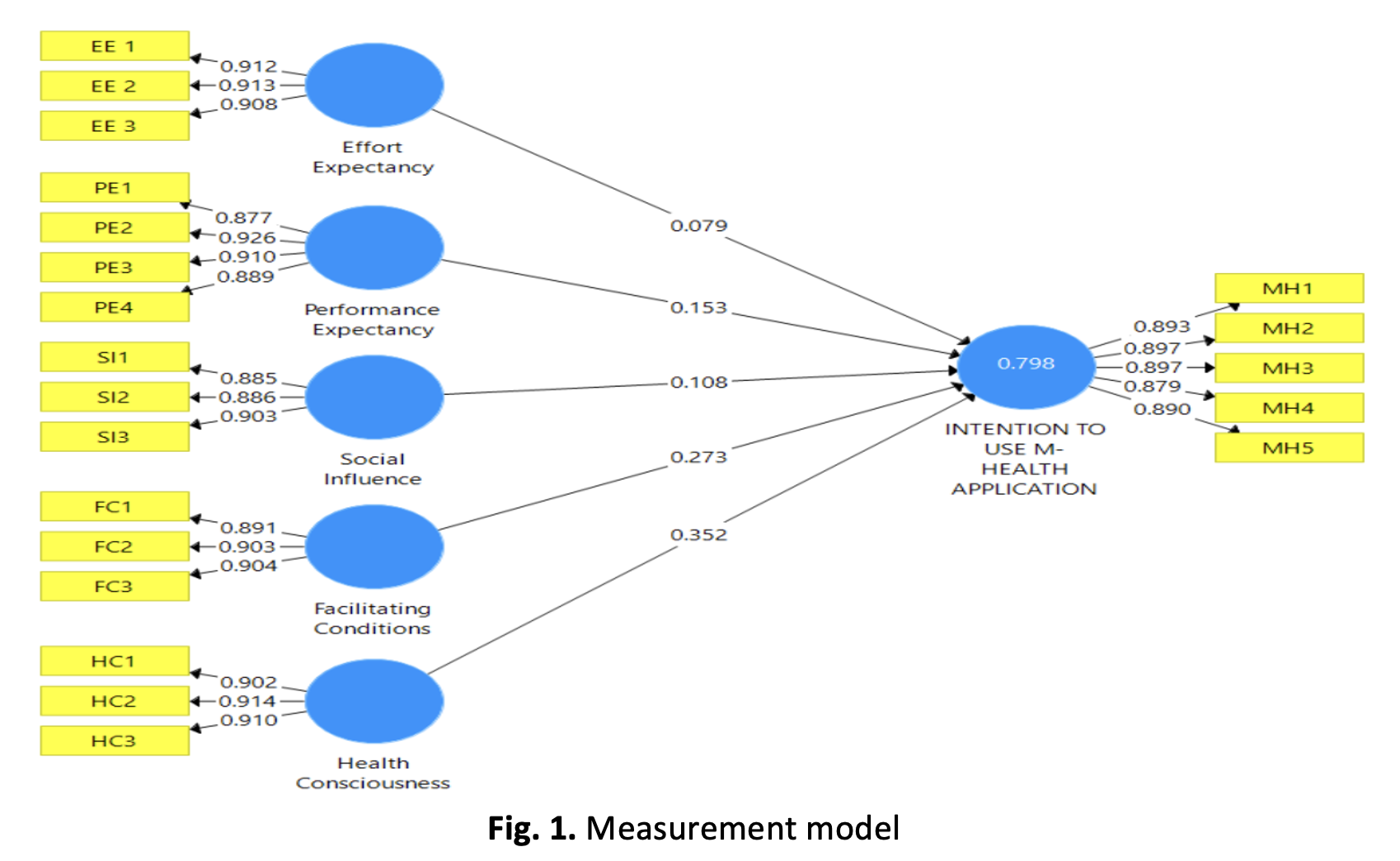
Today’s healthcare system faces several issues, including inefficiency, inequality, and inefficiency. Mobile devices with complex features and user-friendly interfaces have emerged as one of the most important ways to address concerns, opening up new mHealth in the mobile applications industry. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the variables affecting intention to use mobile health applications among young adults in Malaysia. This study used a purposive sampling technique with a correlational cross-sectional research design. The data utilised to empirically assess the suggested model, which is an extension of UTAUT, was collected through an online survey among mobile users. To analyse 312 data sets, smart partial least square was used. The findings revealed that the intention to use mobile health applications is favourably influenced by performance expectancy, facilitating conditions, and health consciousness. However, effort expectancy and social influence do not influence the intention to use mobile health applications. To boost the application of mHealth, it might be necessary for relevant authorities to recognise the obstacles to their use.
Downloads