Reliable and Secure Data Transfer in IoT Networks using Knight-Tour and PHLSB Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.2.107118Keywords:
Internet of Things (IoT), Steganography, Knight- Tour, Polynomial based Hash Least Significant Bit (PHLSB), human visual system (HVS)Abstract
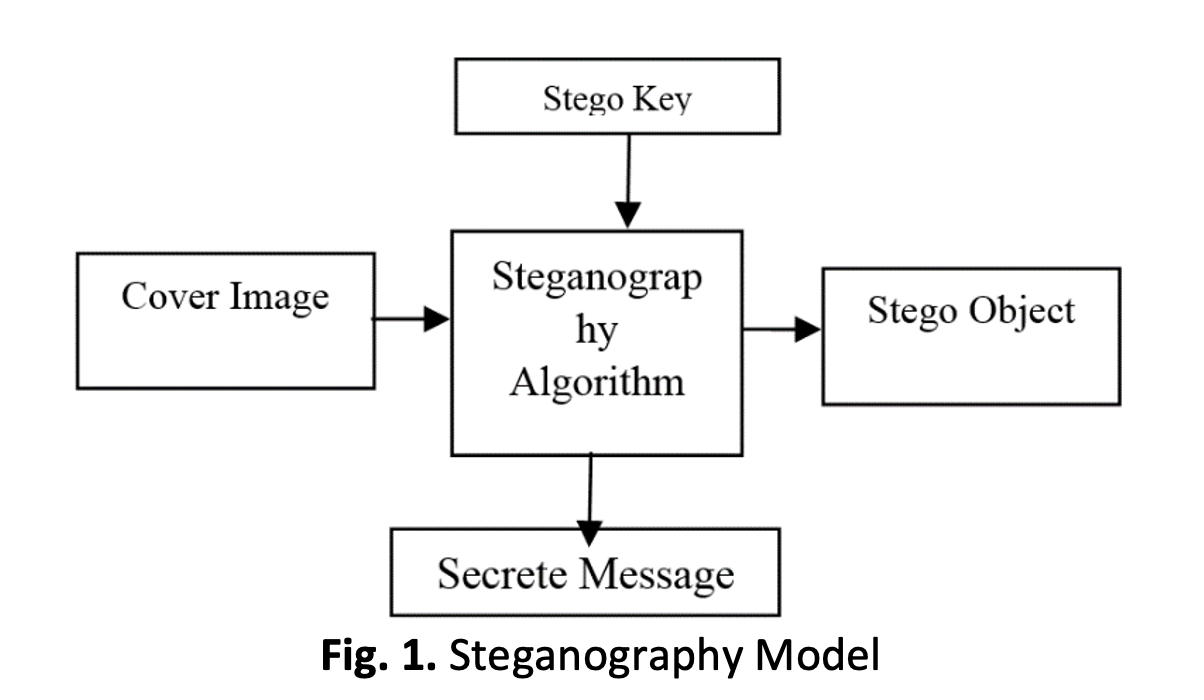
Data security has recently become the most pressing problem for corporate owners and even regular people due to the continual development in the speed of data transmission over the entire Internet, and stricter regulations have been made for data protection. Secure key management is now essential for securing information exchange due to the Internet of Things (IoT) and the rapidly advancing mobile device technologies. Smart home and healthcare IoT apps, for instance, offer automated services to users with little user involvement. Data transmission delays and intrusions can affect existing security solutions that use a single link. In this paper, we propose a novel distributed key management scheme for IoT ecosystem. The methods Knight-Tour and polynomial-based hash least significant bit (PHLSB) that take use of flaws in the human visual system (HVS) are combined to form a hybrid approach to image steganography in this research. The Knight's trip path is a chess board layout that follows the route of a horse without stopping at any of the nodes again. In order to create the scrambled image, this travel path pattern is employed to permute the original image's pixel positions. Prior to being masked behind a cover image, this technique makes sure the communication has been encrypted. A strong mathematical tool is a polynomial equation. The cover object's data was hidden using these equations as a secret key. The suggested solution efficiently secures IoT devices by assigning the resource-intensive encryption processing to local organisations. As a result of the proposed framework's simulation findings, network lifetime PDR (Packet Drop Ratio) has improved, throughput has increased, energy consumption has decreased, and latency has decreased.Downloads
Downloads
Published
2023-09-09
How to Cite
V. Anjana Devi, I. Bhuvaneshwarri, C. Santhosh Kumar, V. Chandrasekar, V. Kalaichelvi, E. Anitha, & Jogendra Kumar. (2023). Reliable and Secure Data Transfer in IoT Networks using Knight-Tour and PHLSB Method. Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology, 32(2), 107–118. https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.2.107118
Issue
Section
Articles




























