Accurate Range Free Location based Partial Derivative and Stochastic Feedforward Neural Network Hyperbolic-based Agriculture Sensor Network Formation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.2.6078Keywords:
Wireless Sensor Networks, Irrigation Management System, Game Theory, Partial Derivative Regression, Laurent Approximation, Stochastic Feedforward, HyperbolicAbstract
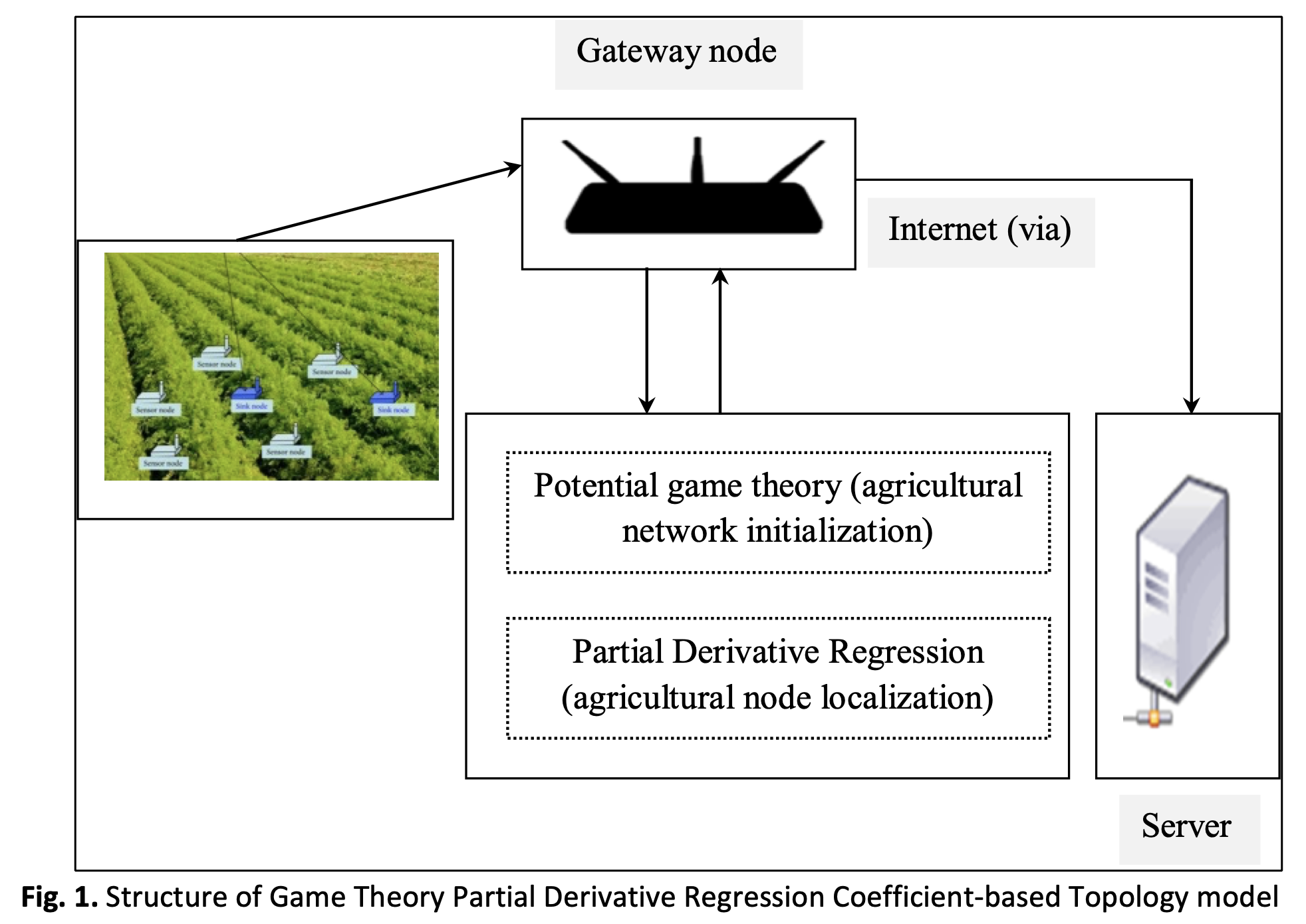
Wireless sensor networks (WSN) authorize the control of different source environmental aspects and crop states as far as precision agriculture is concerned. Nevertheless, the complicated agricultural environment brings about the WSN topology to change often and hence link association likelihood is laborious to predict. Information pertaining to agriculture is an essential distress for localization-based service in the domain of WSNs. Smooth planning and control as the most typical range-free localization method localization performance is said to be good in even distributed networks. Nevertheless, it demonstrated extremely poor accuracy under that in an urgent issue that required to be addressed. In this work a novel topology construction method called, Partial Derivative Laurent Approximation and Stochastic Feedforward Hyperbolic (PDLA-SFH) based Agriculture Sensor Network Formation is proposed. The proposed method is split into three steps. They are agriculture sensor topology construction, average hop size distance validation and position estimation. First topology construction is performed by employing Game Theory Partial Derivative Regression Coefficient-based Topology model. Second, Laurent Approximation-based Hop Size Distance validation model is designed for optimal topology formation. Finally the Stochastic Feedforward Hyperbolic-based Position Estimation is modeled. The simulation results performed in NS3 showed that the proposed localization algorithms can attain better localization performance in terms of accuracy, time and error rate in comparison with other existing methods such as basic Digital Twins and Autonomous Groups Particles Swarm Optimization (AGPSO) under distinct arbitrary network topologies.
Downloads