Content-based Audio Classification System for Bird Sounds
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.33.3.307318Keywords:
content-based audio classification, audio features, native Malaysian bird sounds, MyBird5oundsAbstract
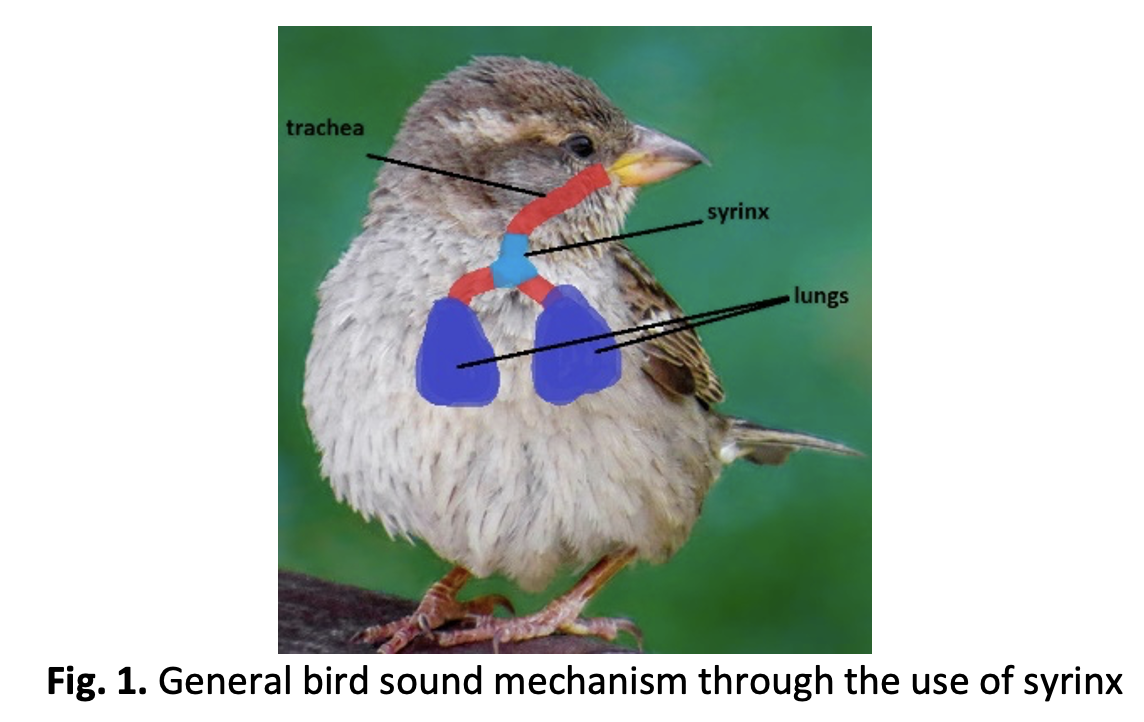
Birds are very important to the ecosystem and an agent in promoting biodiversity. Their vocalizations consist of songs and calls, and are used as a means to communicate, i.e. mating calls, warning calls, etc. This paper aims to automatically classify bird sounds from five native Malaysian birds – the Rhinoceros Hornbill, the Black and Yellow Broadbill, the Common Myna, the Malayan Banded Pitta and the Crested Serpent Eagle. In the initial experiment, the factors that affect the classification accuracy was studied. Results from the initial became the basis of the development of the MyBird5ounds system, a PC-based standalone system that was build using MATLAB. By applying the optimized parameters, classification results were significantly increased. The contribution of this paper lies in the small-scale study that compares the performance of manual bird sounds classification by humans and the automatic classification from MyBird5ounds. 80% classification accuracy was achieved when the optimized parameters were applied – almost twice that achieved in manual classification by trained humans with no prior background in bird watching. This suggests that such a system is beneficial in aiding classification of birds using content-based audio classification methods.
Downloads