Intention to Use Digital Platforms for Islamic Financial Education in Malaysia: Structural Equation Model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.49.1.298311Keywords:
Digital platform, Islamic finance, Financial literacy, Financial education, Financial planningAbstract
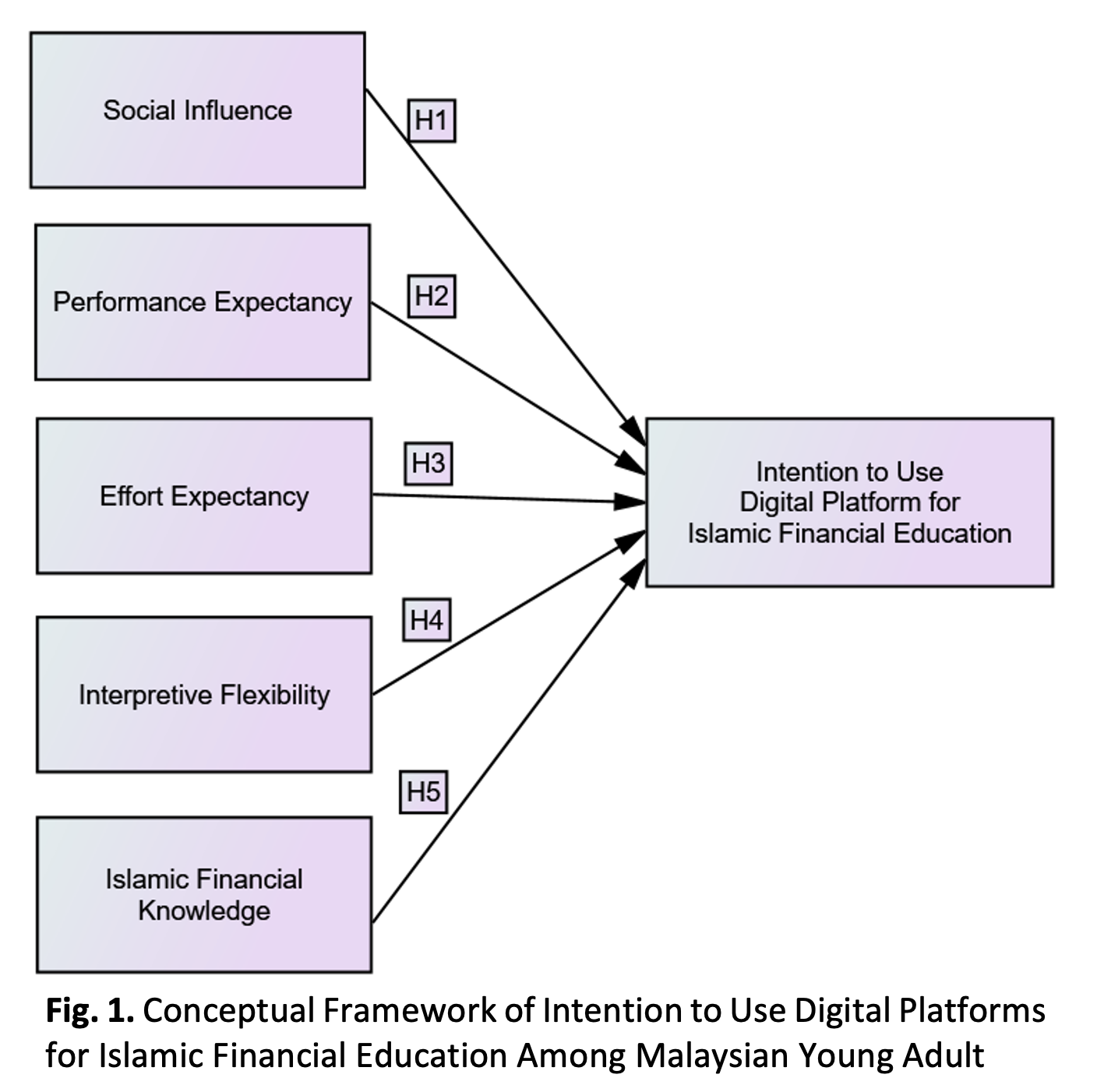
Islamic finance is a practice system that aligns with Shariah obligations, making it different from conventional finance. Besides, Islamic finance and conventional knowledge both positively contribute to the level of financial literacy. It was suggested that financial education is important in elevating financial literacy levels. Furthermore, financial education prepares an individual with the knowledge and skills to make wise financial decisions. As a result, an individual who is uneducated with financial knowledge is exposed to the risk of scams, fraud, and negative financial behaviour such as overspending, impulsive purchasing, unplanned financial action, mismanaging debt, and lack of saving. In addition, Malaysia is known as an Islamic financial hub, which should prioritise the development of Islamic financial education. Alternatively, the advancement of digital technologies has paved the way for the emergence of digital platforms as effective tools in financial education. This study aims to find the factors that contribute to the intention to use digital platforms for Islamic financial education using the structural equation model (SEM) approach. The findings of this study show that social influence, performance expectancy, effort expectancy and interpretive flexibility significantly affect the intention to use digital platforms for Islamic financial education among Malaysian young adults. At the same time, no significant effect is found on Islamic financial knowledge. The findings of this study hope to provide insight into the development of Islamic financial education in future, in addition to helping the Malaysia government to achieve the vision of the Financial Sector Blueprint 2022-2026