Natural Daylighting Assessment on Theoretical Innovative Housing Window in Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.57.2.220233Keywords:
Innovation, Window, Security, Residential, Natural daylighting, Simulation, Sustainability, Performance, MalaysiaAbstract
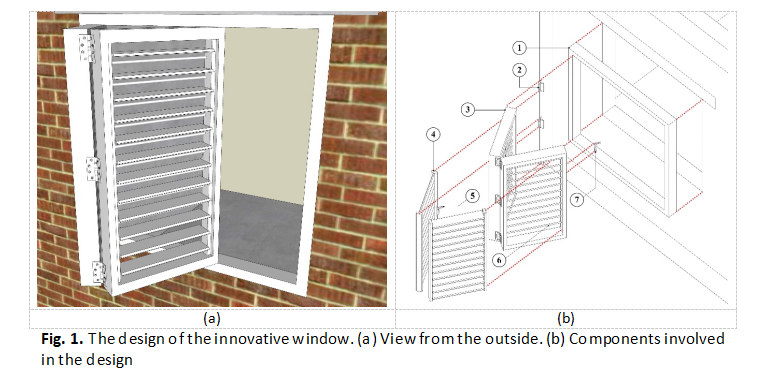
Installation of a bolted window grille in residential building has become a common practice in Malaysia with the aim to improve security aspect, especially against burglary. This feature however resulted in several problems: reducing opportunity to view surrounding outside, affecting building aesthetic, and blocking emergency exit. A theoretical innovative window was proposed to address the issues. The purpose of the research is to assess the performance of the innovation towards natural daylighting. Discussions were conducted with JBPM and local authority to understand legal perspectives of the innovation. Window to Floor Ratio (WFR), Window to Wall Ratio (WWR), and Average Daylighting Factor (ADF) were investigated through Sefaira building simulation. 3 guidelines were referred in this research: MB206 – Approval Form to Construct a Small-scale Building (MB), UBBL 1984, and Malaysian Standard MS 2680: 2017. 7 models were constructed to identify the performance of the innovation in every possible form and operation. Overall, there are several operations of the innovation were failed to sustainably perform. With a small alteration involving materials and dimensions, the innovation can successfully allow natural daylighting to take place.