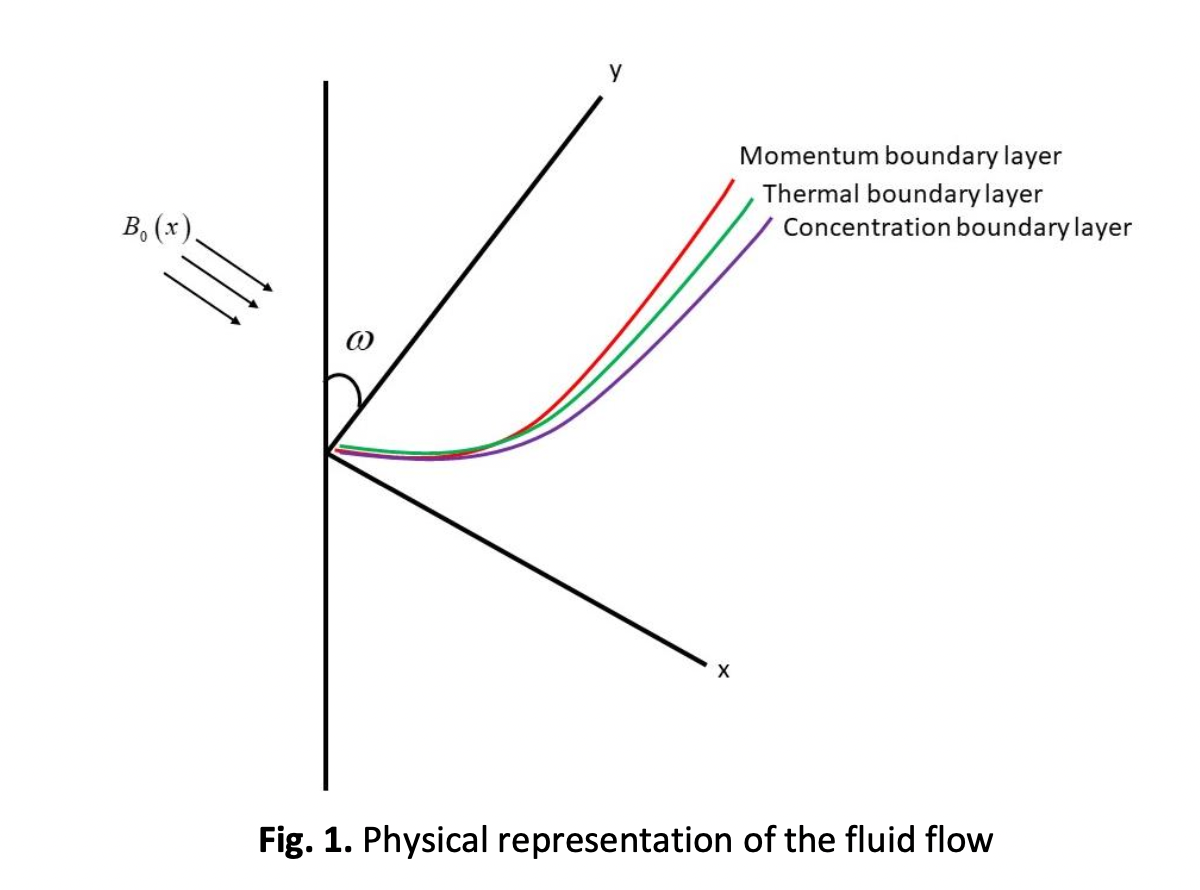
MHD Mixed Convective Non-Newtonian Stagnation Point Flow Over an Inclined Stretching Sheet: Numerical Simulation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.102.1.7384Keywords:
MHD, stretching sheet, stagnation point, Casson fluidAbstract
This paper includes numerical simulation upon MHD mixed convective heat transfer properties of stagnation point flow across an angled stretched sheet. Boundary value problem is solved using similarity transformation approach with shooting technique. The impact of different corporeal constraints like mixed convection parameter, thermal radiation parameter, chemical reaction parameter, Brownian motion and thermophoresis, Casson parameter upon velocity and temp profile as well as skin-friction coefficient , Nusselt number, Sherwood number on velocity, temp concentration profile are shown graphically. Casson parameter increases velocity and diminishes temperature profile. Chemical reaction term decreases Sherwood number and increases concentration profile.
Downloads