Hydraulic Model for Flood Forecasting of Tajabad Khwar in Hayatabad Phase III Peshawar, Pakistan: A Case Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.89.1.160174Keywords:
Hydraulic Model, Flood forecasting, Arc GIS, Flood mapping, Hydrological ModellingAbstract
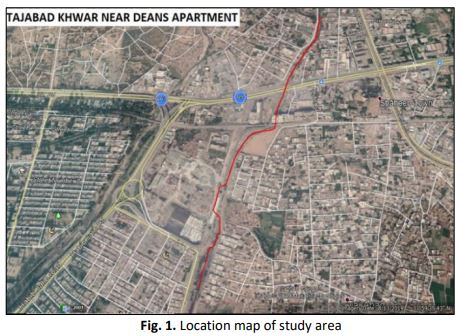
Among all other natural disasters occurring throughout the world, floods are considered to be the worst and most devastating catastrophe as it causes loss of billions of lives. Flooding is caused due to inundation of water over the areas which are in close proximity of river or natural waterways resulting in severe damages to commercial and residential areas in the surrounding. Thus, an efficient flood forecasting system through the development of a combined hydrological and hydraulic model for the prediction of future flood events through marking the potential high-risk zone is required to minimize the damages. Due to large number of encroachments made in the waterway of Tajabad khwar located near Deans Residential Apartment of Hayatabad Phase III, a hydraulic model is developed for its flood forecasting as the floods in this khwar may cause severe damages to the inhabitants of the adjacent areas. In this research work, Flood zone maps are developed for 10 years, 20 years, 50 years, and 100 years flood return periods in order for deterring extent of the inundation as a result of these encroachments and to identify the areas at potential risk. Flood discharge for each return period was estimated using HEC-HMS software and was found to be 772, 1036, 1392 and 1666 m^3/sec for 10 years, 20 years, 50 years, and 100 years flood return periods respectively. The corresponding water surface elevation determine using HEC-RAS and was found to be 196 m, 197m, 201m, 202m. This model provides a basic idea for developing flood zone maps of a given period of return for the assessment of areas that can get adversely pretentious by floods.
Downloads