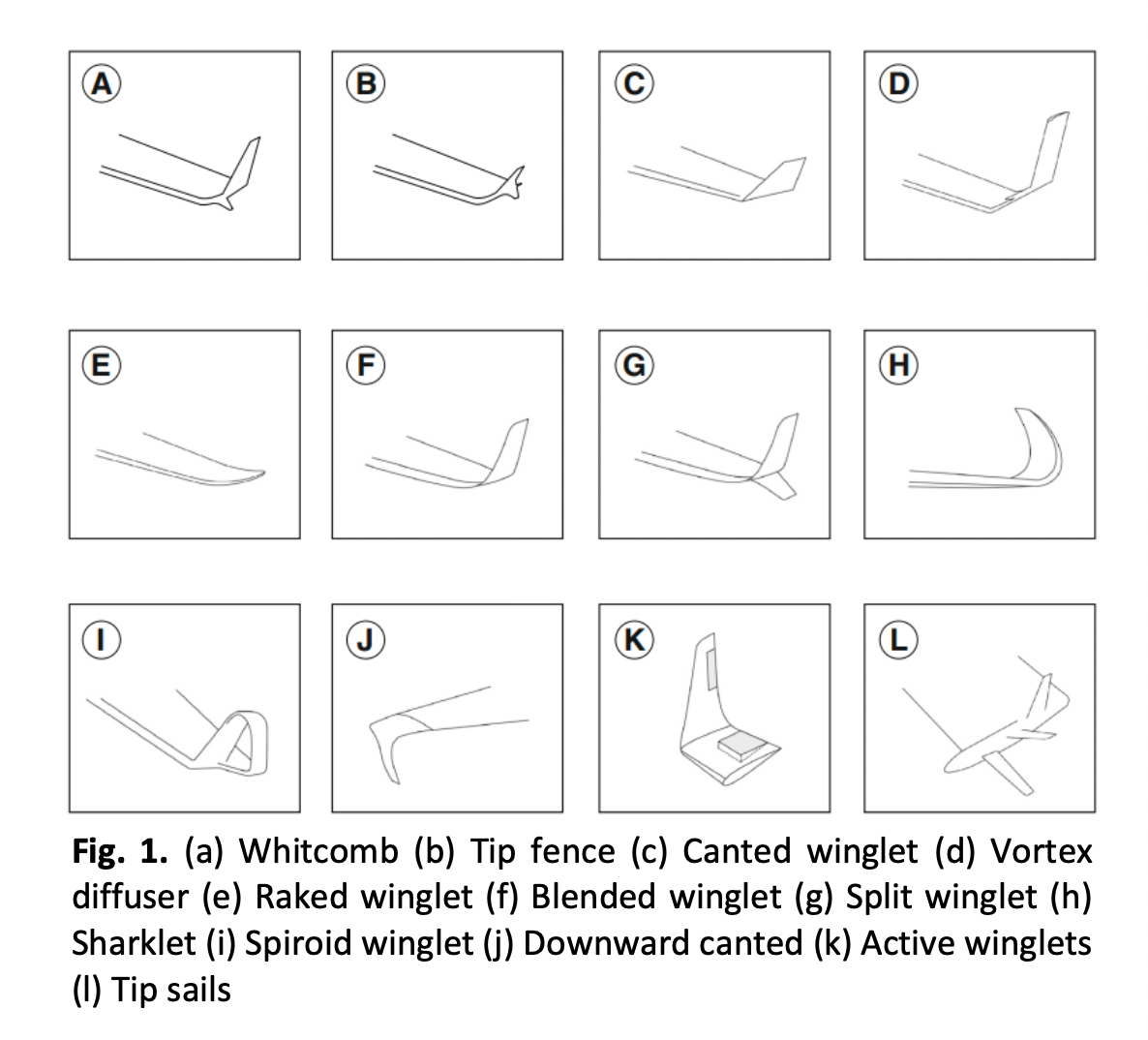
Aerodynamic Characteristics of Blerak Winglet
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.103.2.4054Keywords:
Aerodynamic performance, BLERAKE winglet, ANSYS Fluent, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), lift and drag coefficientAbstract
The induced drag created by wingtip vortices has a significant impact on aircraft performance. Winglets are wingtip extensions that are intended to reduce the creation of vortices and increase the fuel efficiency. The present study is based on analyzing different winglets planform for aircraft at various angles of attack (AOA) to improve the aerodynamic efficiency. The Finite Volume Method in pressure-based solver along with the Realizable k - ɛ turbulence model, with standard atmospheric boundary conditions is used to do the CFD computations in ANSYS Fluent. According to the findings, an optimized BLERAK (Blended + Raked) winglet from the present study has a substantial impact on aerodynamic efficiency when compared to conventional winglets, and it is projected to yield a higher lift-to-drag ratio. The blerak winglets model gives 1.5 to 2% drag reduction than the other winglet models at angle of attack variations of 8°, 12° and 16°.
Downloads