Thermal and Degradation Analysis of Electrospun Polyurethane Prepared using Radiation Induced Grafting
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.108.2.110121Keywords:
Electrospinning, Polyurethane, Radiation Induced Grafting CopolymerizationAbstract
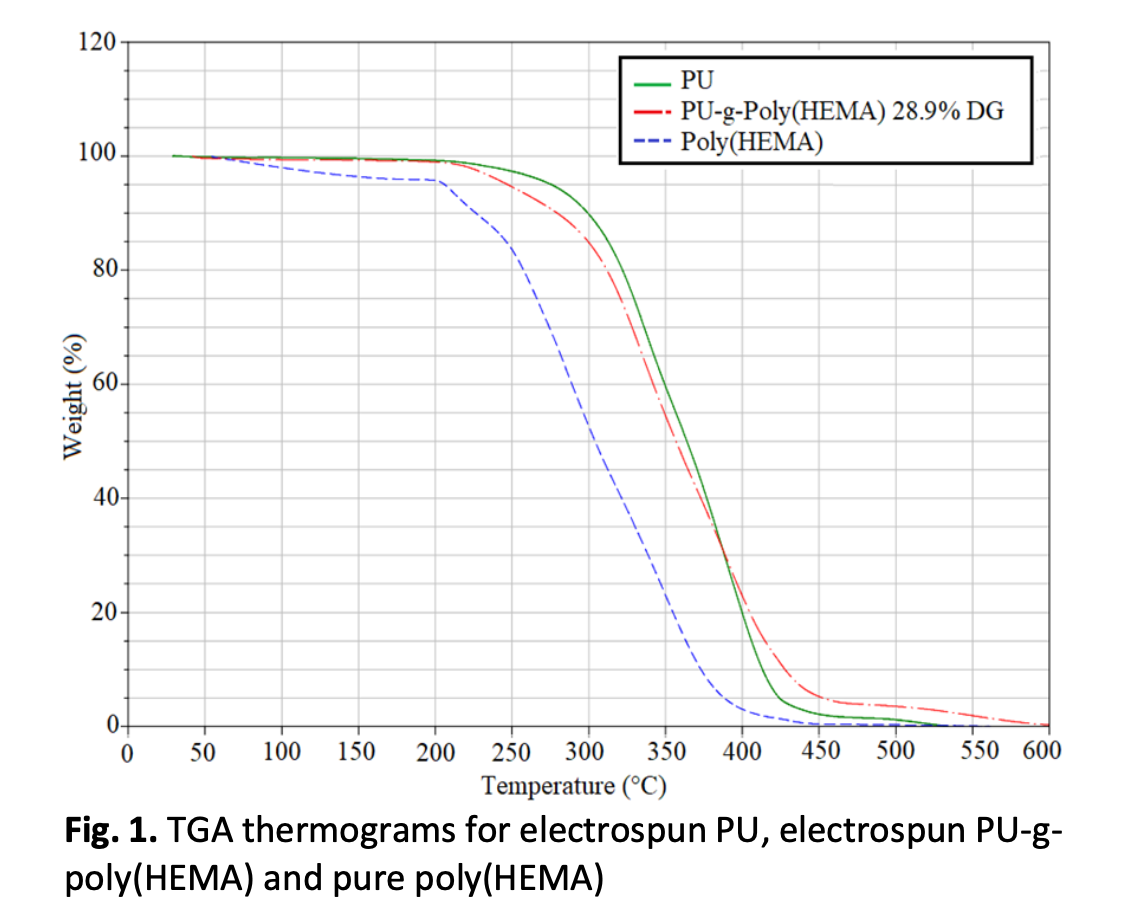
Polyurethane (PU) membranes was prepared using electrospinning followed by modification with 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) by radiation-induced grafting (RIG) copolymerization method via electron beam. The lack of knowledge of polymer properties of PU-based membrane prepared using RIG method need for dedicated study. Thus, the effect of thermal stability, in vitro degradation, water uptake analysis, and surface morphology after 84 days’ incubation times toward grafted PU-g-poly(HEMA) membrane was evaluated for the first time using thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), analysis of mass, percentage of water uptake and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), respectively. Based on the DTGA curves, the electrospun PU exhibits two-stage of deposition. After grafted with HEMA, the first stage of decomposition was shifted to the lower temperature, and the second stage of decomposition was shifted to a higher temperature. At 500 °C, PU grafted with HEMA leaves residue about 3.526% more elevated in value than original material of PU, which is 1.151%. Degradation test showed that a higher percentage degree of grafting was lowering the percentage of weight loss. SEM images supported the morphology observation shows no noticeable changes such as cracked or eroded has occurred. In conclusion, electrospun PU grafted with HEMA was improved its thermal stability, stable in swelling properties and was found competent to degrade slowly in phosphate buffer saline (PBS). The results show that PU-g-poly(HEMA) exhibits better thermal stability than pure poly(HEMA) and the amorphous regions give the polymer toughness and could be up-and coming candidates for tissue engineering including artificial blood contracting medical devices.
Downloads