Cellulose Acetate/Polyethylene Glycol Composite Beads for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.108.2.3147Keywords:
Cellulose acetate, polyethylene glycol, adsorbent, methylene blue, composite beadAbstract
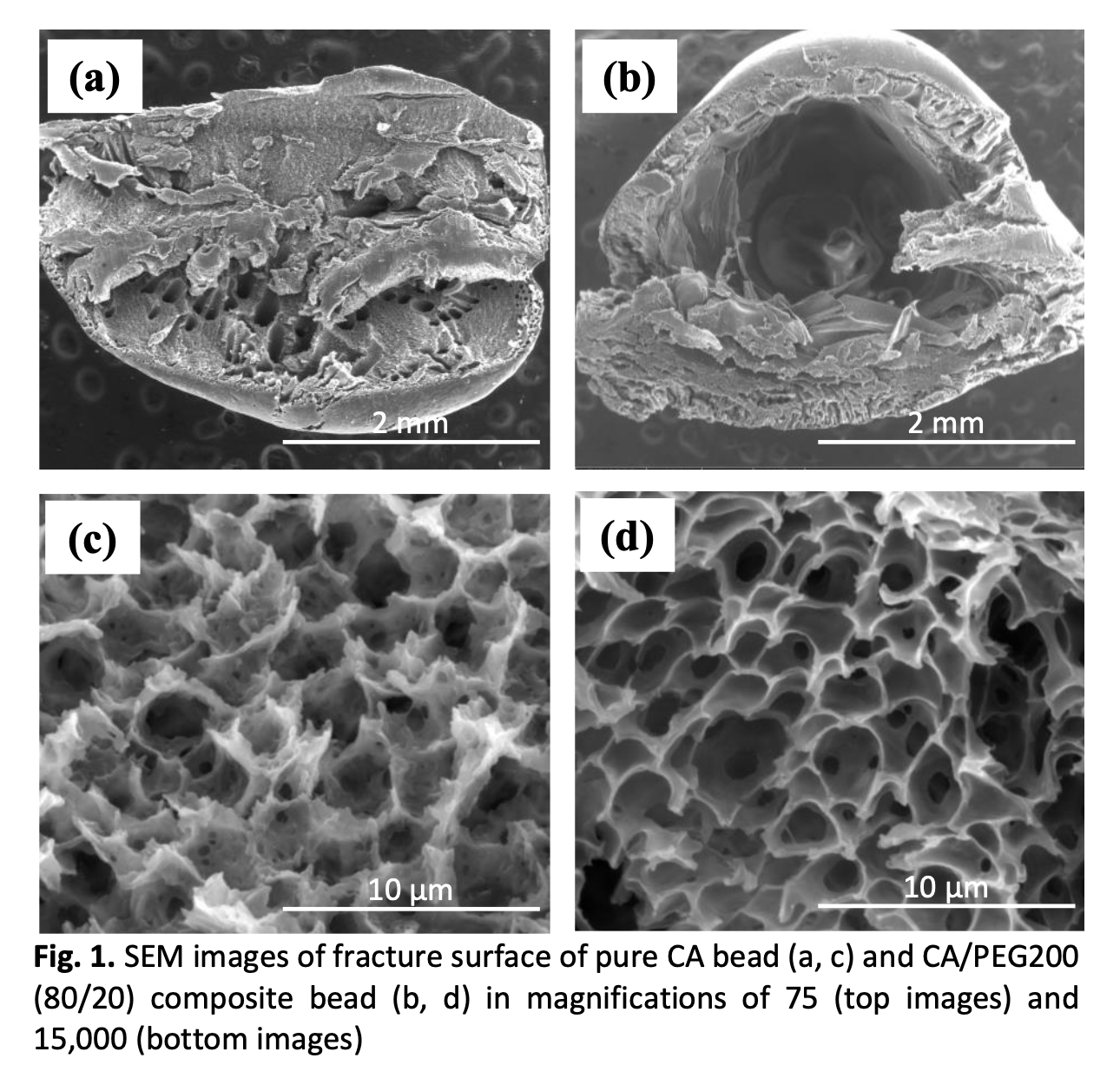
The development of eco-friendly and biodegradable adsorbent with excellent adsorption performance is of great importance for the efficient dye removal in wastewater. Herein, an efficient and biodegradable composite adsorbent bead was fabricated from cellulose acetate (CA) modified with low molecular weight polyethylene glycol 200 (PEG200) for the adsorptive removal of methylene blue dye (MB) from aqueous solution. The weight fraction of PEG was varied to investigate the effect of material bead composition on the morphology, molecular structure, crystal phases, thermal stability, mechanical properties, and adsorption performance of the composite beads. Batch adsorption was carried out at various times to estimate the time at equilibrium adsorption capacity and kinetic model. Various operating conditions such as pH, initial MB concentration, and adsorbent dosage in experiment were also executed to examine the adsorption performance of this system. The result showed that all beads have porous structure and the pore size increase after the addition of PEG200. The adsorption capacity and % MB removal generally showed an improvement with the rise of PEG content. The batch adsorption experiments demonstrated that the best % removal and adsorption capacity of MB were 93.35 % and 28.005 mg/g, respectively, that was obtained by composite CA/PEG200 (80/20) bead at pH of 11, initial MB concentration of 30 mg/L, and bead dosage of 1 g/L. The adsorption kinetic fitted well to Elovich-kinetic model with average R2 of 0.844. Overall, this work offers new finding into the development of effective, environmentally friendly, and inexpensive cellulose-based adsorbents for wastewater remediation.
Downloads