Experimental Investigation of Direct Solar Photovoltaics that Drives Absorption Refrigeration System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.106.1.116135Keywords:
Diffusion absorption refrigeration, Ammonia-Water, renewable energy, technology PV systemAbstract
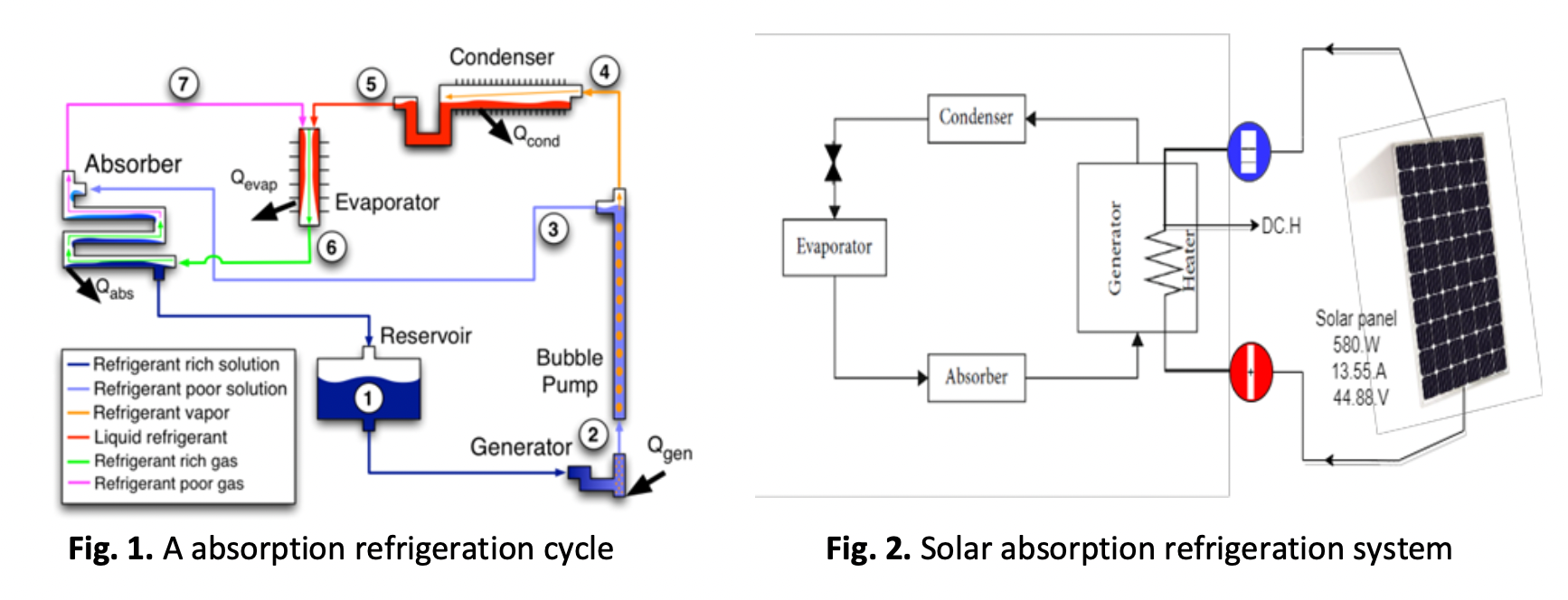
Renewable energy used for refrigeration applications has become essential very recently due to the fossil fuel crisis and the global warming problem. Moreover, using photovoltaic PV to generate electricity than using inverters and energy storage represents a high-cost process. This study aims to investigate the opportunity of using PV output directly to operate a refrigeration system. The absorption refrigeration system uses heat as an energy source for the generator that drives the system. Moreover, the absorption refrigeration system doesn't have a compressor but a generator. As a result, the novel aspect of this study is the use of PV electricity's DC output to power the heater that provides the needed heat for the generator without the use of an inverter that provides AC electricity. The essential very difference here is that the compressor needs a consistent and steady electric supply. However, using DC electricity for heating is not very restricted if the voltage fluctuates a bit. A 580 W PV was used to power a refrigerator with a capacity of 70 liters. During several tests, the freezer of the fridge reached -26 C and the cabin temperature was around 10 C. This finding was similar to the performance of this fridge on a conventional heater.
Downloads