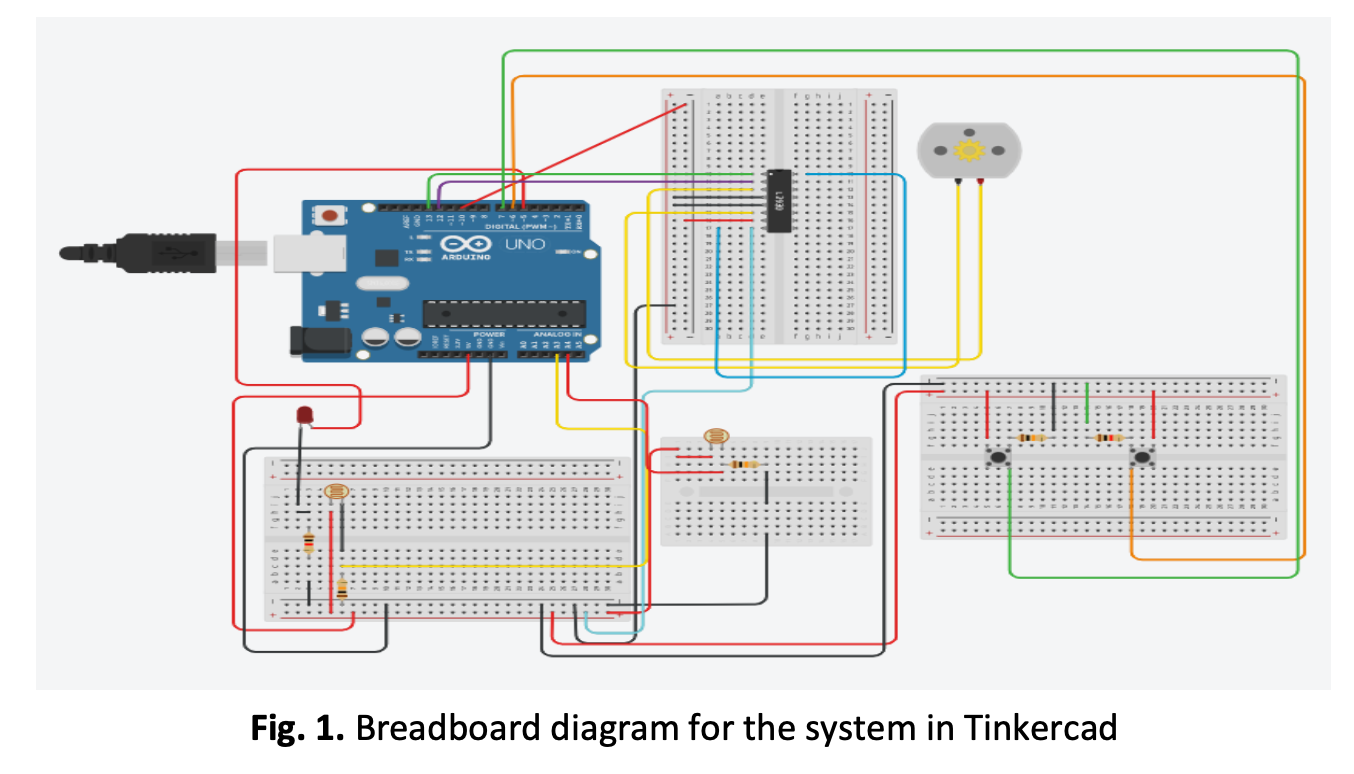
Simulation Study of a Smart Factory Lighting and Shading System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.98.1.116124Keywords:
Lighting analysis simulation, lighting system, shading system, power-savingAbstract
Insufficient and uneven light distribution in the workplace affect the quality of work that requires high precision. In addition, inadequate lighting not only affects the health of workers but is also linked with a condition called 'Sick Building Syndrome'. The artificial light in factories is commonly manually controlled, resulting in energy wastage. Hence this paper presents a smart lighting and shading system to create both comfort lighting and energy-efficient factory environment. Three-dimensional modelling simulations were built using Tinkercad and Revit. The control system built utilizes the motorized skylight solar shades and the artificial high LED Bay, which able to adapt with the fluctuating factory lighting condition. If the light enters the factory through the motorized shade on the factory ceiling is insufficient or uneven, the artificial light will be switched on. The implementation of both mechanisms managed to improve the light distribution evenness and keep the light intensity level in the factory in the range between 885 lux and 1306 Lux from 9am to 6pm, while from 6pm onwards at average of about 900 lux. Furthermore, the electrical energy consumption is reduced significantly during the daytime as the control system has utilized the sunlight as part of the light source for the factory. The smart system can save as much as 22.39%, or 55.2128kWh from 9am to 7pm. In conclusion, the smart lighting and shading control system has proven the effectiveness theoretically, and the objectives were achieved.
Downloads