Investigation of the Influence of Ambient Conditions on the Thermodynamic Characteristics of Air as a Working Fluid for Gas Turbines
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.106.1.182196Keywords:
Specific heat capacity, temperature, relative humidity, humid air, isentropic exponentAbstract
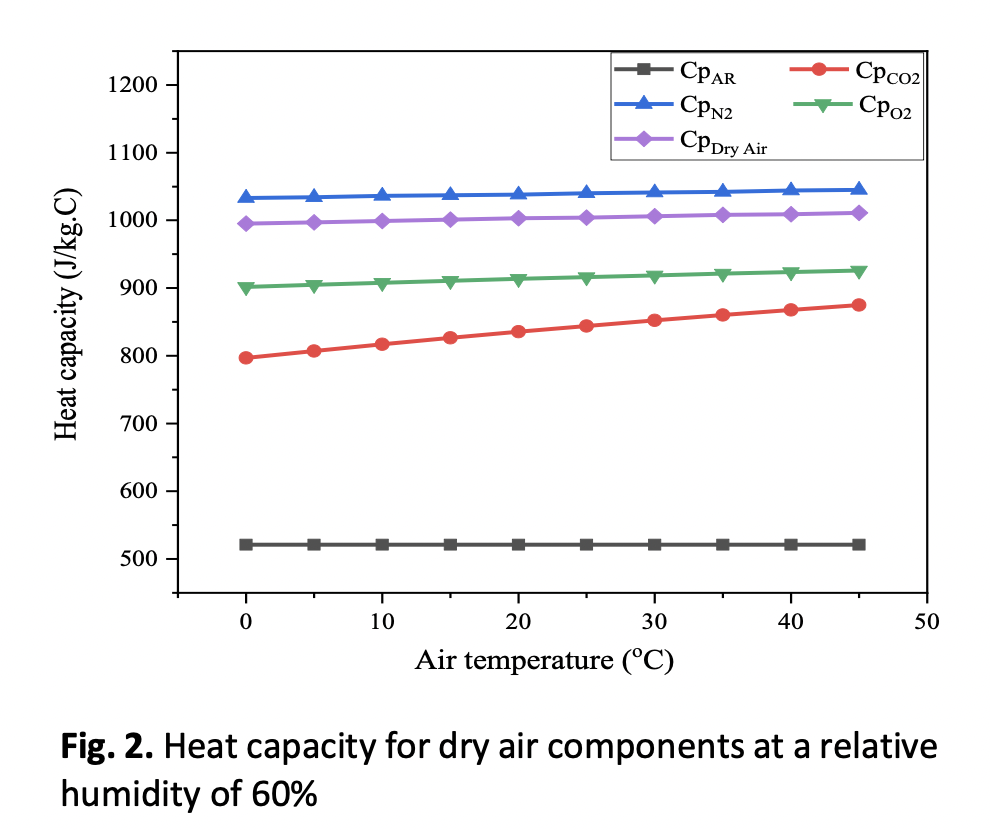
The study focuses on estimating thermodynamic characteristics at constant pressure for ambient air as a working fluid for gas turbines. The objective of this paper is to carry out a thermodynamic analysis of the properties of air as a working gas for a power plant. Various values of relative humidity, as well as temperatures, were examined in this study. Code was written using EES (Engineering Equations Solver) to conduct the simulation. This code contains the necessary equation to compute the thermodynamic characteristics of the working fluid. According to the results, both temperature and relative humidity remarkably influence the specific heat capacity (C_p), isentropic exponent (γ_h) as well as the gas constant of air (R_h). According to the results, when the ambient air temperature is increased from 0 to 45 ℃ with constant relative humidity values of either 10% or 90%, the specific heat capacity increases by 5.01% and 17.6%, respectively. Furthermore, the isentropic exponent decreases by 1.07% and 4.5%, respectively. The results show that the gas constant of air increases with ambient air temperature and relative humidity. One can conclude that the ambient conditions have considerable influence on the thermodynamic characteristics of a gas turbine working fluid.
Downloads