Influence of TiO2 and Al2O3 Nanoparticles Addition on Thermal, Wettability and IMC Growth of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Lead-Free Solder at Different Reflow Temperature
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.109.1.188195Keywords:
Lead-free solder, nanoparticles, intermetallic compound, nanocompositeAbstract
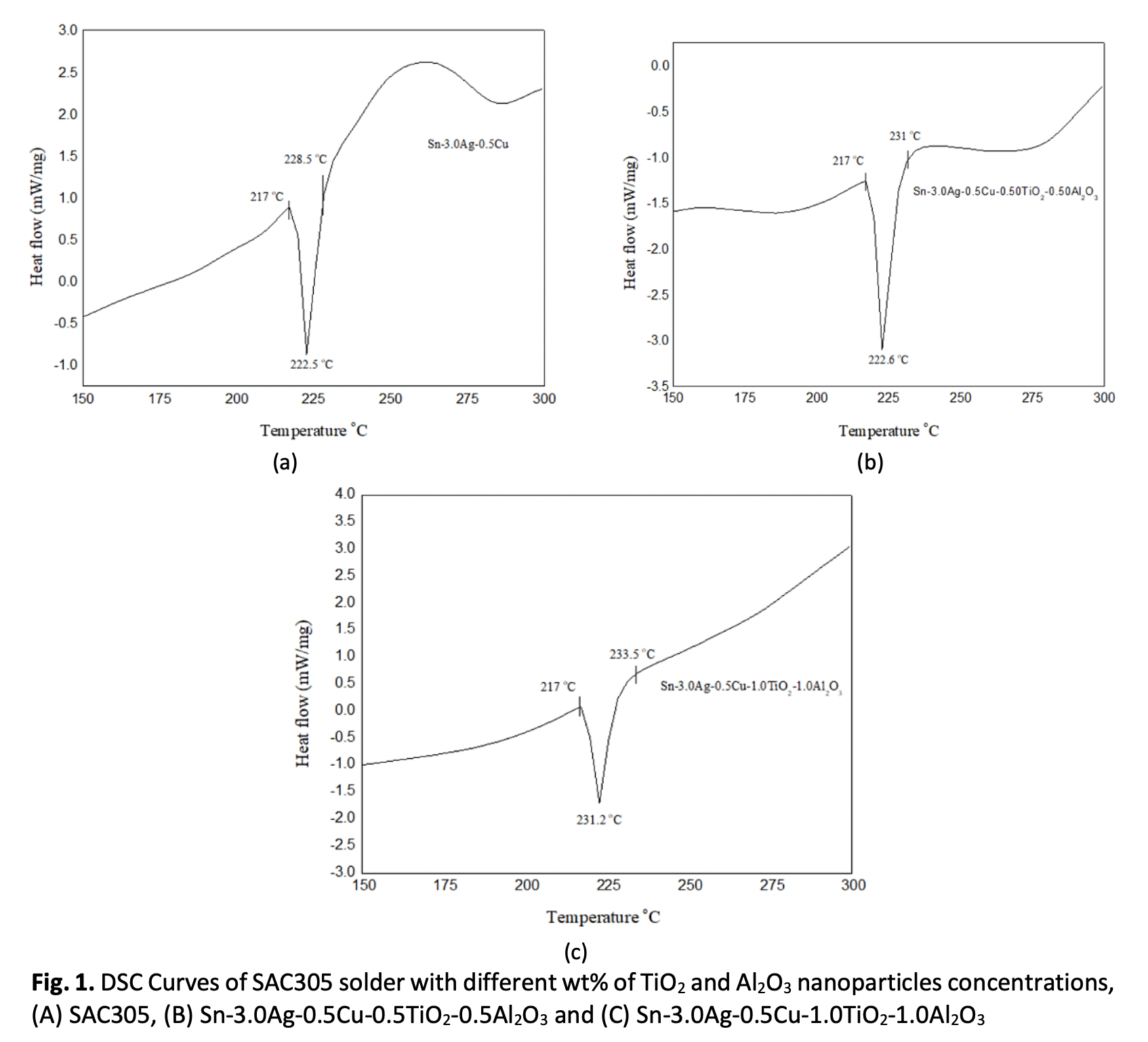
This study investigated the influence of adding 0.50 wt% and 1.0 wt% titanium dioxide (TiO2) and aluminium oxide (Al2O3) nanoparticles on the properties of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu (SAC305) lead-free solder alloy. In terms of thermal properties, SAC305 lead-free solder with or without addition of TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles, the melting temperature is very similar and comparable. The wetting performance of the SAC305 nanocomposite solder was determined by the contact angle. The best contact angle recorded is 31.65° at reflow temperature of 250°C for 0.50 wt% addition of TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles. The thickness of the IMC layer was observed using an Optical Microscope and measured. Results show that the thickness of the IMC layer decreased when TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles were reinforced into the SAC305 solder system, which shows significant decrease when 0.50wt% of TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles were added. However, beyond 0.50 wt% the thickness of IMC layer increases along with increasing reflow temperature. The results reveal that the adsorption effect of TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles will restrict the growth of the IMC layer under controlled concentration of the nanoparticles and reflow temperature. The optimal parameters to enhance the performance of SAC305 solder by reinforcing TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles are reflowed at 250°C at 0.50 wt% concentration of TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles.
Downloads