Numerical Investigation of Semi-Empirical Relation Representing Standard Deviation in Nusselt Profile Due to Water Jet Impingement
Keywords:
Nusselt number, Reynolds number, nozzle-target spacing, standard deviationAbstract
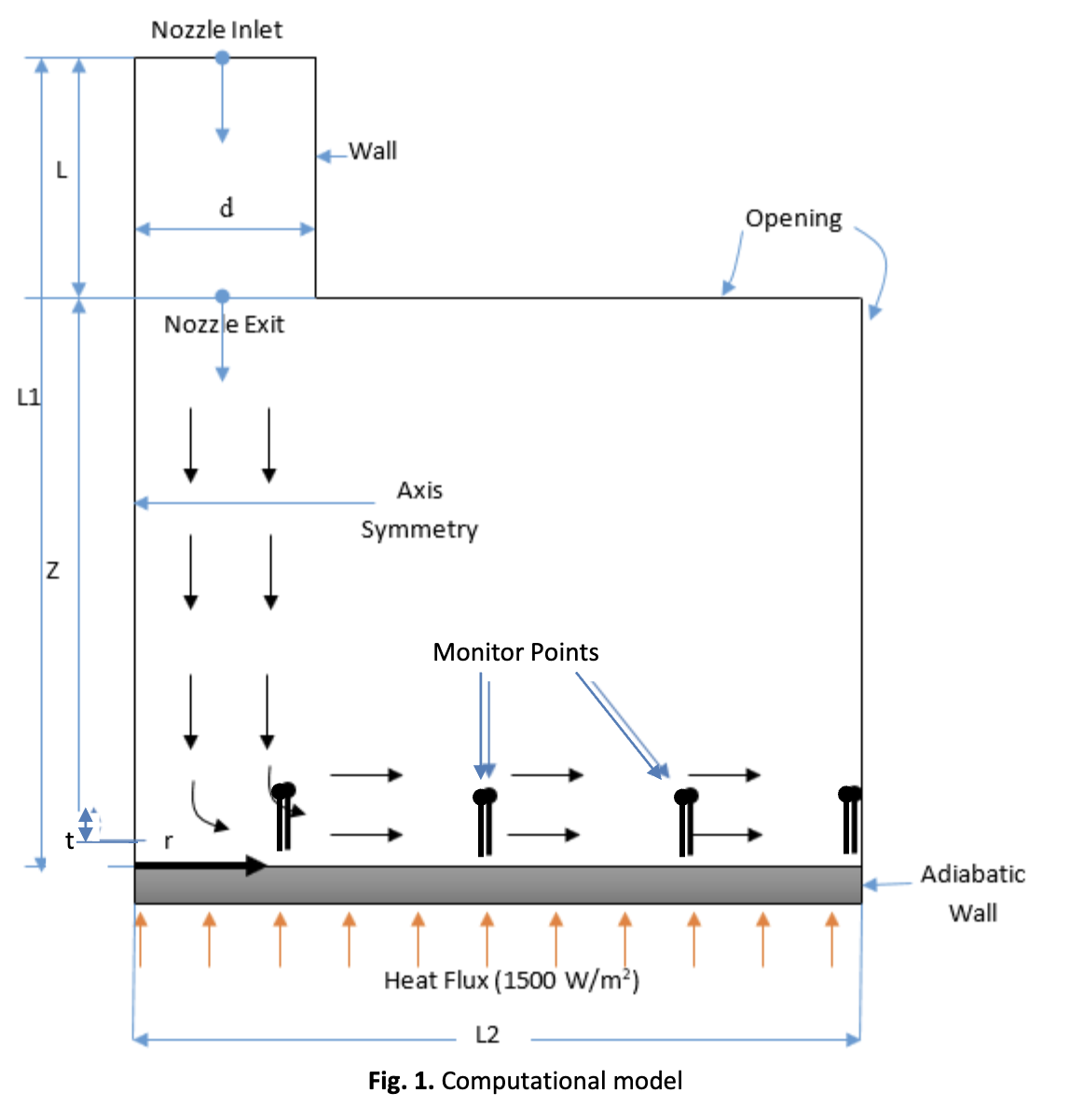
Use of water jets in material processing industries is finding pace. Water jets are used for cooling of materials due to its high convective heat transfer coefficient. Nusselt number is the parameter used for studying the heat transfer rate through water jet impingement. Simulations are performed and Nusselt magnitudes are plotted for Reynolds number 2000, 2200, 2400, 2600, 2800, 3000, 3200 and 3400 at constant nondimensional nozzle target spacing (z/d) 4. Also, Nusselt distribution is obtained at z/d = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 at constant Reynolds value of 750. The standard deviation (STDEV) of Nusselt magnitude is arranged according to constant C (C = Re/ (z/d)) for regression analysis. The semi-empirical relation representing standard deviation (STDEV) in terms of C is found out to be ???????????????????? = 14.751 × (????) 0.917 . Also, SST + Gamma-Theta turbulence model is found to predict accurate results
Downloads