The Investigation of Thermoacoustic Methods for Nanofluid Stability on Heat Exchanger
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.109.1.114125Keywords:
Thermoacoustic methods, nanofluids stability, coefficient convectionAbstract
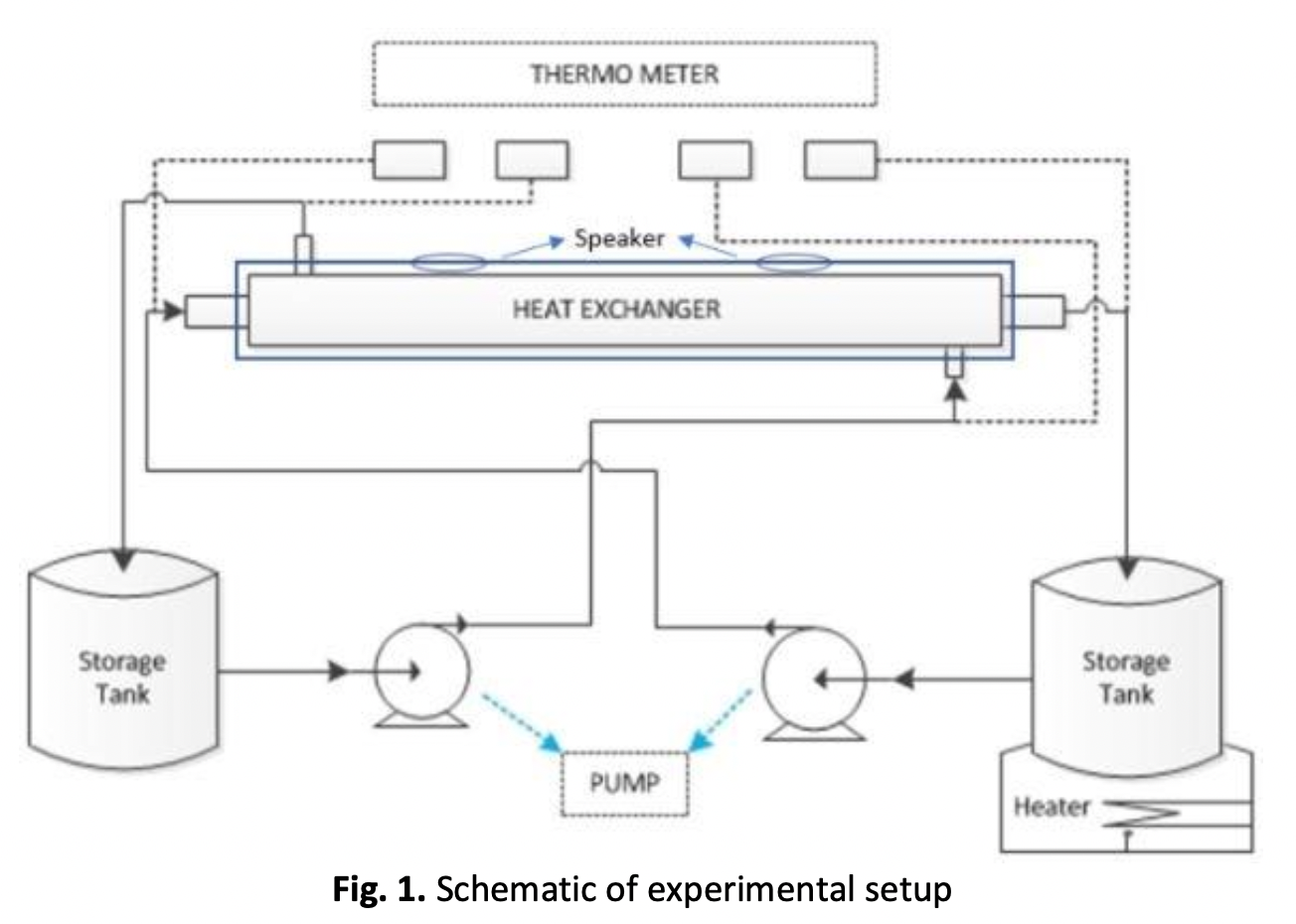
Due to various engineering applications, nanofluids have gained much attention in the last decade. A Nanofluid is a nanometer-sized particle such as metal, oxide, carbide, etc., dispersed into a base heat transfer fluid. The heat exchanger is a device to transfer heat between fluids. Heat exchanger plays a very important role in modern industry. The new innovative fluid called nanofluid is introduced to improve the overall heat transfer and heat transfer rate. Thermoacoustic is a system which uses sound waves and a non-flammable mixture of inert gases to generate an effect. This paper investigates the enhancement of the heat transfer coefficient of a nanofluid containing alumina (Al2O3) nanoparticle with a volume fraction of 0.4% and sonification at 100 Hz, 500 Hz and 1000 Hz. The addition of Al2O3 nanoparticles will affect the characteristics of the nanofluids, which affect the values of density, specific heat, thermal conductivity, and dynamic viscosity. And the addition of the thermoacoustic method with the sonification of acoustic waves can stabilise the effect of Brownian motion in the nanofluid flow. The maximum results are obtained using acoustic waves at 1000 Hz at high temperatures.
Downloads