Combined Effects of Chemical Reaction and Radiation on MHD Squeezing Flow of Casson Fluid
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.111.1.5879Keywords:
Chemical reaction, radiation parameter, squeezing flow, viscous dissipation, slip boundaryAbstract
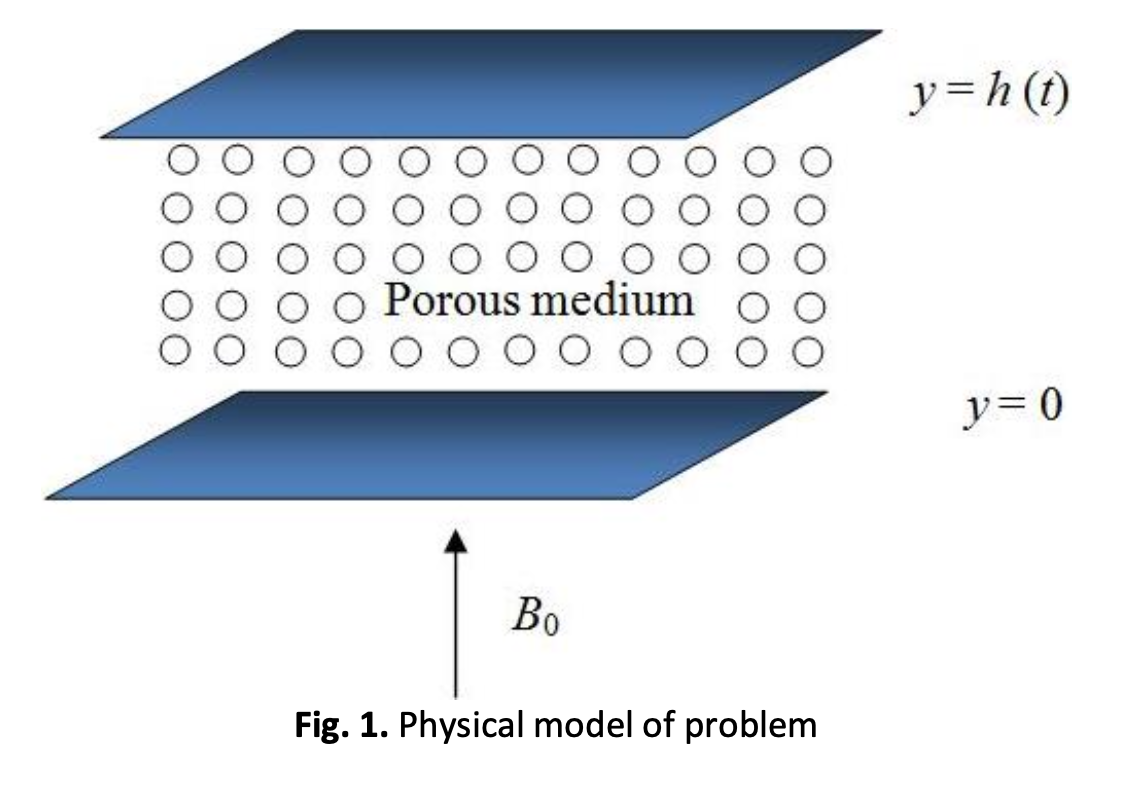
The impacts of chemical reaction on the magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) squeezing Casson fluid flow through a porous medium under the slip condition with viscous dissipation the presence of radiation parameter have been discussed. The flow is produced when two plates are compressed together in close proximity to one another. Using similarity variables may successfully convert partial differential equations (PDEs) to ordinary differential equations (ODEs). The shooting technique was used to perform the numerical analysis, which entailed solving the competent governing equations with dominating parameters for a thin liquid layer. This was done to determine the results of the study. It is essential to evaluate the numerical results in light of previously conducted research to validate the current answers. According to the results, an increase in the distance between the two plates leads to a rise in the velocity and the wall shear stress. The gas's velocity, temperature, and concentration all drop due to an increase in the Hartmann and Casson parameters. Both the temperature and the rate of heat transfer rise in direct proportion to the amount of viscous dissipation. In addition, it has been shown that the rate of mass transfer rises during destructive chemical interactions, but during constructive chemical reactions, the contrary occurs, which results in adverse effects.
Downloads