Improve the Performance of Integrated Collector Storage-Solar Water Heater by using Glazing Confined Air Space: A Numerical Simulation Approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.111.2.4364Keywords:
Solar heater, CFD analysis of integrated collector storage-solar water heater, performance of integrated collector storage-solar water heater, thermal efficiencyAbstract
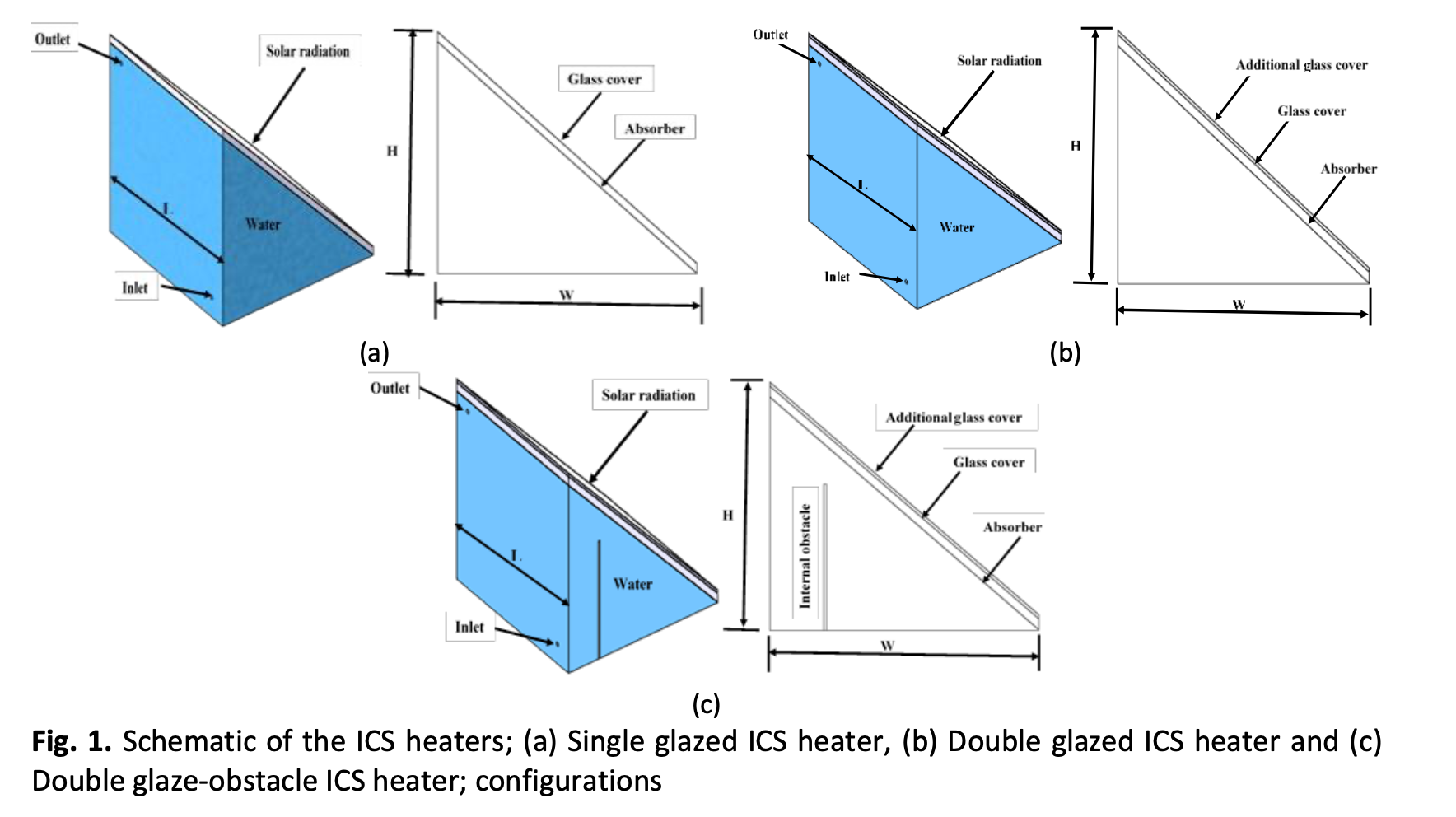
A numerical study is presented by double-glazed the conventional rectangular integrated collector storage-solar water heater with internal obstacle in the storage container which improving the performance and making them convenience for household uses. A three-dimensional, laminar and unsteady numerical simulation with the aiding of COMSOL 5.5 software is used to investigate three shapes of integrated collector storage-solar water heaters (single glazed, double glazed, and double glaze-obstacle). The governing equations which represented of conservation equations of mass, momentum and energy. The performance of these systems was tested along two days in February and July during different atmospheric conditions at Kufa-Iraq. In these days, the water temperature reached a maximum value of 61.02 ℃ for no-load condition when the tap temperature was 39.3℃. Obstacle and glazed integrated collector storage –solar water heater shows the higher performance as compared with the two other heaters with a maximum value of instantaneous efficiency of 59.95 % in February.Also, the average Nusselt number and heat transfer between the absorber plate and confined air decreases and this increase a storage water temperature. In general, the total efficiency under no-load conditions is lower than on load case. The results were compared to previous theoretical and experimental work and show a good agreement with a maximum error that not exceeds to (4.24 %).
Downloads