Significance of Melting Heat Transfer, Inclined Magnetic Field, and Thermal Radiation on the Dynamics of Williamson Nanofluid Above a Stretching Sheet
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.111.1.4157Keywords:
Williamson fluid, bvp4c, radiation, inclined magnetic fieldAbstract
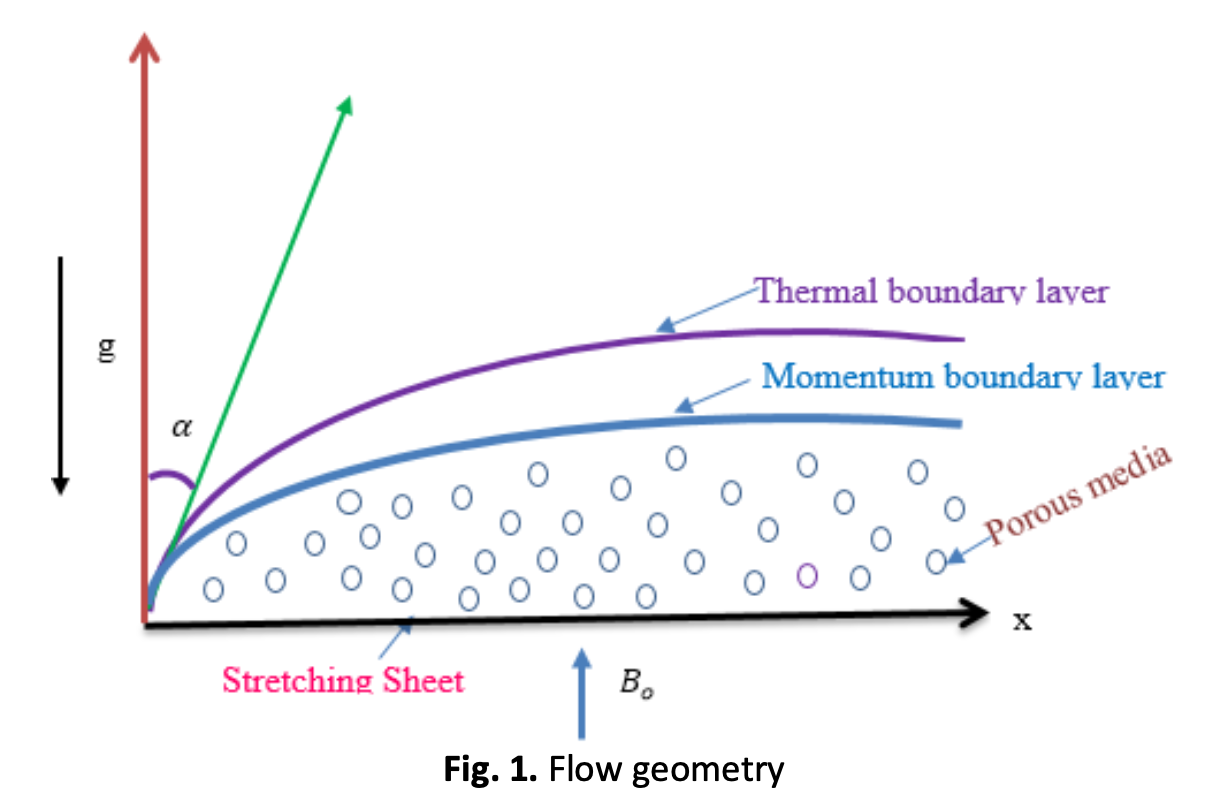
This study investigates the melting heat transfer in MHD flow that occurs when the flow is past a stretched sheet. With the use of the boundary layer concept, a set of non-linear ODEs is derived from a system of PDEs of motion and energy. After transforming the non-linear ODEs and their boundary conditions into dimensionless form with the use of appropriate similarity conversions, the equations are then numerically solved by employing the MATLAB inbuilt solver bvp4c method in conjunction with the shooting methodology. Through the use of a variety of charts and tables, the authors analyze and describe in depth the effects that relevant factors have on a variety of flow fields. As melting factor (Me) increases, it is discovered that the effect of Me on fluid temperature and velocity distributions decreases. Williamson parameter and inclined magnetic profile are shown to have decreasing impact on velocity and momentum parameter. After that, the findings are compared with the earlier published findings in limited situations of the issue, and it is discovered that they are in exceptional specify with those findings.
Downloads