Numerical Solution of EMHD GO-Fe3O4/H2O Flow and Heat Transfer over Moving Riga Plate with Thermal Radiation and Heat Absorption/Generation Impacts
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.112.1.6275Keywords:
EMHD, shrinking surface, hybrid nanofluid, graphene oxideAbstract
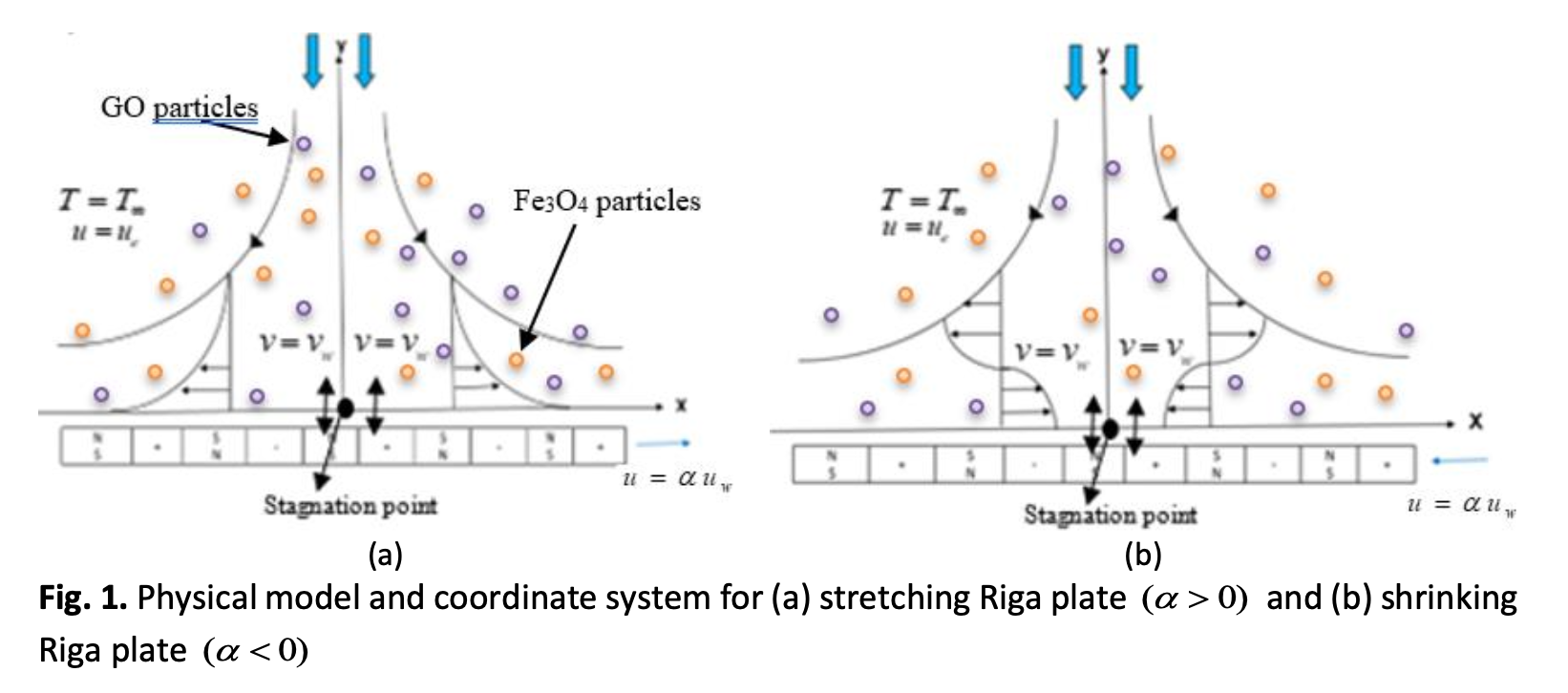
The importance of thermal radiation impacts on electromagnetohydrodynamics (EMHD) hybrid nanofluid movement and heat transference towards stretching/shrinking surface is investigated. The influences of external effects such as suction, heat absorption and generation are also being considered. The hybrid nanofluid chosen for exploration is Graphene Oxide (GO) and Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) as nanoparticles, while water (H2O) is a base fluid. The mathematical modelling in partial differential equations (PDEs) is formulated to ordinary differential equations (ODEs) for simplicity using an appropriate similarity variable. The solution of the reduced ODEs is then computed with the help of bvp4c solver built-in MATLAB software. The findings reveal that the magnetic field augmented the velocity profile, while thermal radiation affects the temperature profiles to amplify. The heat generation and absorption upsurged the heat transfer for GO-Fe3O4/H2O with accompanying effects like plate thickness. It is also worth mentioning that GO-Fe3O4/H2O enhanced skin friction and heat transfer by about 3.2% and 1.6%, respectively, more than Fe3O4/H2O.
Downloads