Computational Modelling of the Aerodynamic Noise of the Full-Scale Pantograph of High-Speed Trains
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.93.1.94109Keywords:
High speed train, Pantograph aerodynamics, Computational aeroacoustics, Computational fluid dynamics, Aerodynamic noiseAbstract
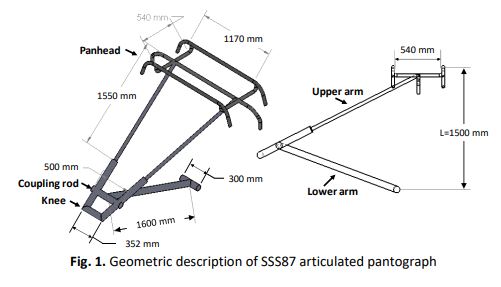
High speed rail systems have significantly developed due to the increased demand on the rail transportation in the recent years. The necessity for enhancing the environmental sustainability of the rail systems imposed many challenges for the researchers to decrease the level of noise generated by the high speed rail systems. This paper aims to investigate the aerodynamic noise of the pantograph of the high-speed trains in different operating conditions. Computational fluid dynamics technique was used to assess the acoustic noise of the pantograph components. Three-dimensional computational simulations were performed using FLUENT software. Comprehensive analyses of the acoustic pressure and the air velocity distributions were accomplished for the detailed full-scale pantograph components. A modified model for the pantograph was introduced to reduce the aerodynamic noise of the pantograph’s panhead. Good agreement was found between the obtained results and the reported results in the literature. Different design profile for the collector was then presented as a possible solution for the reduction of both the aerodynamic noise and the reduction of the fluctuating forces at the panhead-catenary interaction, which affects the quality of the power transmitted to the high-speed train. Vortex shedding was the main source of noise at the pantograph panhead and knee. Based on the obtained computational results, it was found that the use of an elliptic-edge cross-section bars can be a potential modification in the collector shape that can reduce the aerodynamic noise at the panhead.
Downloads