Investigating the Palm Oil Mill Wastes Properties for Thermal Power Plants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.88.2.113Keywords:
Palm oil wastes, biomass, coal, empty fruit bunch (EFB), mesocarp fiber, palm kernel shell (PKS), thermal power plants, co-firing, renewable energyAbstract
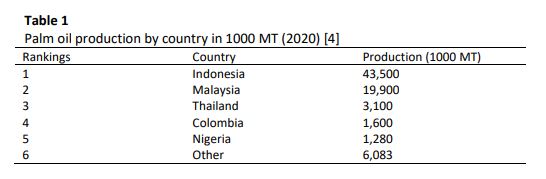
Renewable energy is a reliable solution for addressing global warming and fossil fuel depletion issues. Due to the abundance of biomass resources, such as palm oil wastes, which are currently underutilised, this is an opportunity for Malaysia to seize and implement this renewable energy solution for power generation. Palm oil mill wastes, such as empty fruit bunch (EFB), palm mesocarp fibre (PMF), and palm kernel shell (PKS), are worth to be investigated as a possible feedstock for combustion in thermal power plants. Co-combustion or co-firing of biomass in coal-fired thermal power plants offers a significant potential to reduce harmful emissions and represents a low cost and low-risk method. This paper aims to review and compare existing biomass thermal combustion technologies globally to evaluate the potential of utilising palm oil waste with coal. Before undergoing various pretreatment options, it is necessary to understand the feedstock characteristics for thermal power plant combustion. It is recommended to implement the combustion of palm oil wastes with coal in Malaysia to reduce harmful pollution. Based on the findings, Malaysia appears to be on the right track to optimise the use of palm oil wastes for electricity generation. The enhanced usage will reduce the negative impact of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
Downloads