Numerical Study of Subaortic Stenosis and Pannus Formation on Blood Flow Around Mechanical Heart Valves
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.95.2.180190Keywords:
Mechanical heart valve, CFD, heart valve disease, thrombus, pannusAbstract
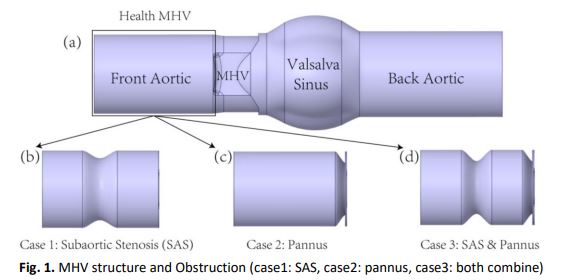
Patients after mechanical heart valve implantation are prone to complications. Mechanical heart valve obstruction is a rare but life-threatening complication. Obstruction may include thrombosis, pannus formation around the valve, or both. However, the relationship between thrombus and pannus and mechanical heart valve hemodynamics has not been thoroughly studied. We studied the fluid dynamics of thrombus and pannus formation through numerical simulations and provided detailed information about the interaction between complications and related prosthetic valves so that complications can be detected early. Studies have shown that the formation of thrombus and pannus leads to significant changes in the peak transvalvular velocity of the artificial valve, the transvalvular pressure gradient, and the corresponding hemodynamic indicators. As the height of the thrombus and pannus increases, the jet velocity and transvalvular pressure gradient will increase accordingly. When obstruction exceeds 20%, the impact increases significantly under the same percentage of obstacles. When the obstruction percentage is over 30%, the rest at least doubled. The results also indicate that SAS obstruction has the most significant impact on the blood flow of MHV. At the same time, it should be noted that when SAS and pannus are combined, the ring form vortex in front of the pannus has a potential risk of accelerating the deterioration of the pannus.
Downloads