Automation of Bio-Hydrogen Gas Production in a Fed-Batch Microbial Electrolysis Cell Reactor by using Internal Model Control of Neural Network
Keywords:
Microbial electrolysis cell, internal model control, hydrogen productionAbstract
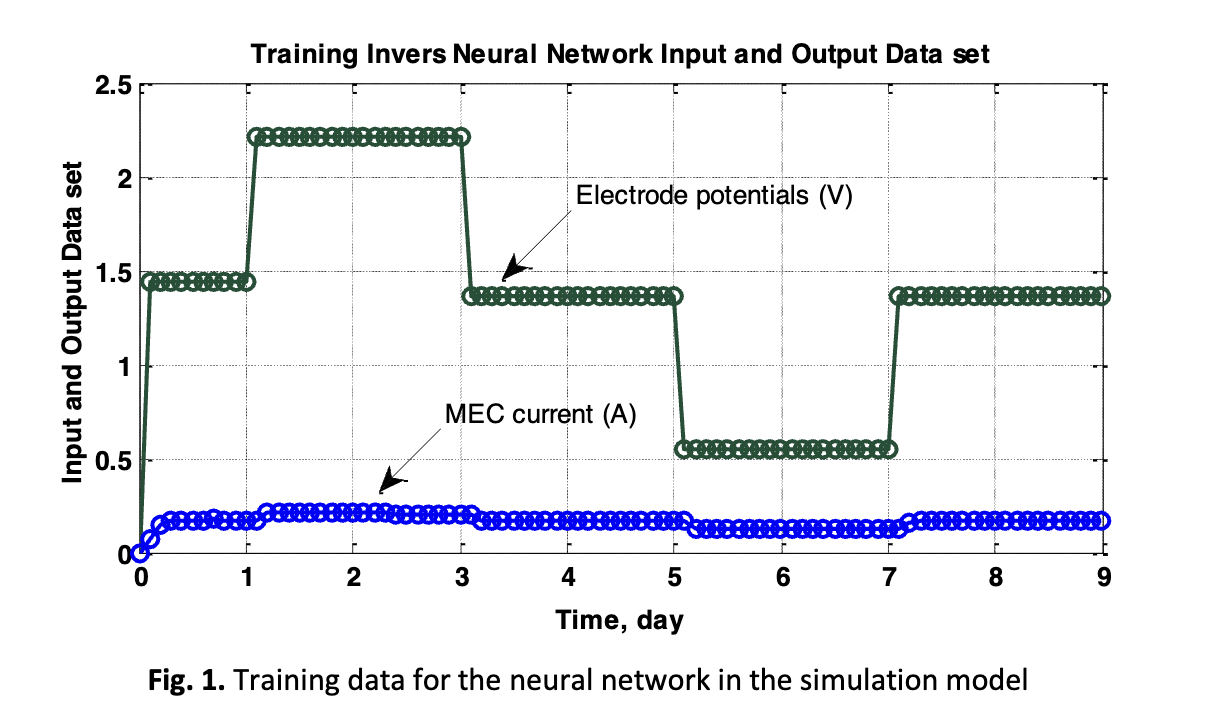
Microbial Electrolysis Cell (MEC) is an environmentally friendly technology for hydrogen production in which a bio-electrochemical process occurs with catalysts of microorganisms. The microorganisms oxidize all organic matters in a fed-batch MEC reactor of hydrogen gas production. The production of hydrogen electron exchange occurs continuously by rising the cathode potential. The amount of energy used in hydrogen gas production from organic matter is much less than the one from water by electrolysis. The MEC process is a complex and highly nonlinear because of the microbial interactions, and it makes the system difficult to optimally operate and control. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) was used to model the MEC process, and it was reliable model with coefficient correlation of validation, R2 being 0.915. To control the current and voltage of MEC, two controller of Proportional-Integral-Derivative Ziegler-Nichols (PID ZN) and Internal Model Control of Neural Network (IMC NN) were applied. The comparative study on both controllers with the controller output being in an optimal current and voltage to the MEC process was conducted in Matlab software. As the result, the IMC NN controllers provided the best control performance.
Downloads